India’s Neighbours – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: India’s Neighbours and MCQs Questions: India – Size And Location (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “India’s Neighbours” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 9th chapter 1 “India – Size And Location“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 1 India – Size And Location Notes PDF
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 1 India – Size And Location Notes PDF for a concise, students-first summary of this foundational unit. It explains latitude and longitude, India’s continental position, extent, and neighbors with simple maps and memorable examples. Use the one-page checklist to memories coordinates, standard meridian, and border facts.
Short diagrams clarify scale and distance problems, and quick practice questions mirror board patterns. Perfect for last-minute revision or classroom recap, the PDF helps you understand why India’s size and location matter for climate, transport, and strategy – without unnecessary fluff. Download it and revise confidently.
India’s Neighbours
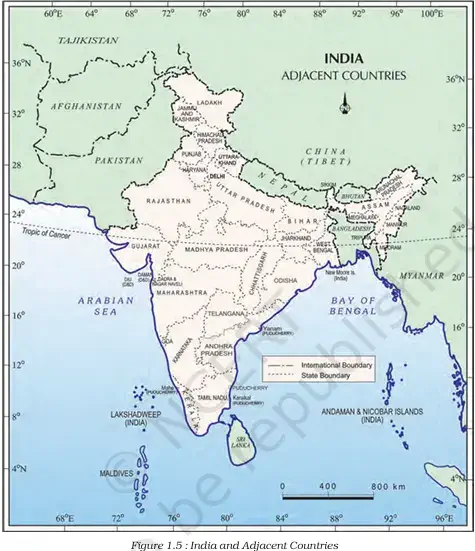
1. India’s Strategic Position:
- India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia.
- India has 28 states and 8 Union Territories.
2. Land Boundaries:
- India shares its land boundaries with 7 countries:
a. Northwest: Pakistan, Afghanistan
b. North: China (Tibet), Nepal, Bhutan
c. East: Myanmar, Bangladesh
3. Maritime Neighbours:
- India’s southern neighbours across the sea are:
a. Sri Lanka
b. Maldives - Sri Lanka is separated from India by:
a. Palk Strait
b. Gulf of Mannar - Maldives Islands are located south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
4. Links with Neighbours:
- India has had strong geographical and historical links with her neighbours.
- On the physical map of Asia, India stands apart from the rest of the continent.
5. Do You Know? (Extra Exam Facts):
- Before Independence (1947):
a. There were two types of states in India:
b. Provinces → directly ruled by British officials appointed by the Viceroy.
c. Princely States → ruled by hereditary local rulers, accepted British sovereignty in return for autonomy. - Modern Educational Initiative:
a. School Bhuvan (NCERT) – a map-based learning portal.
b. Purpose: Create awareness about natural resources, environment, and sustainable development.
c. Initiative of Bhuvan – NRSC/ISRO.
d. Based on NCERT syllabus.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Geography Class 9 Chapter 1: India – Size And Location
| Topics No. | Topics Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Location |
| 2 | Size |
| 3 | India And The World |
| 4 | India’s Neighbours |
MCQs on NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 1 Topic – India’s Neighbours
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “India’s Neighbours” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. How many states and Union Territories does India have?
a) 29 states and 9 Union Territories
b) 27 states and 7 Union Territories
c) 28 states and 8 Union Territories
d) 26 states and 9 Union Territories
Answer: c) 28 states and 8 Union Territories
Question 2. Which two countries share their boundaries with India in the northwest?
a) Nepal and Bhutan
b) Pakistan and Afghanistan
c) Bangladesh and Myanmar
d) Sri Lanka and Maldives
Answer: b) Pakistan and Afghanistan
Question 3. Which countries share their boundary with India in the north?
a) Pakistan, China and Sri Lanka
b) Nepal, Bhutan and Myanmar
c) China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan
d) Afghanistan, Bhutan and Bangladesh
Answer: c) China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan
Question 4. Which countries share their boundary with India in the east?
a) Myanmar and Bangladesh
b) Afghanistan and Bhutan
c) China and Sri Lanka
d) Pakistan and Maldives
Answer: a) Myanmar and Bangladesh
Question 5. Which island countries are India’s southern neighbours?
a) Maldives and Bhutan
b) Sri Lanka and Maldives
c) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
d) Lakshadweep and Sri Lanka
Answer: b) Sri Lanka and Maldives
Question 6. Which sea channel separates Sri Lanka from India?
a) Arabian Sea
b) Bay of Bengal
c) Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar
d) Laccadive Sea
Answer: c) Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar
Question 7. Maldives Islands are situated to the south of which Indian islands?
a) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
b) Lakshadweep Islands
c) Sri Lanka
d) Minicoy Islands
Answer: b) Lakshadweep Islands
Question 8. Before 1947, how many types of states existed in India?
a) One type
b) Two types
c) Three types
d) Four types
Answer: b) Two types
Question 9. Who ruled the provinces of India before 1947?
a) Local hereditary rulers
b) British officials appointed by the Viceroy
c) Indian National Congress leaders
d) Zamindars and landlords
Answer: b) British officials appointed by the Viceroy
Question 10. Who ruled the Princely states before 1947?
a) Indian Nationalists
b) Zamindars
c) Local hereditary rulers
d) Governors of British India
Answer: c) Local hereditary rulers
Question 11. On what condition did Princely states acknowledge British sovereignty?
a) In return for independence
b) In return for financial aid
c) In return for local autonomy
d) In return for military protection
Answer: c) In return for local autonomy
Question 12. Which organisation has developed the portal “School Bhuvan, NCERT”?
a) CBSE
b) ISRO (NRSC)
c) UGC
d) NCERT alone
Answer: b) ISRO (NRSC)
Question 13. What is the purpose of the School Bhuvan, NCERT portal?
a) Entertainment
b) Political awareness
c) Map-based learning of natural resources, environment and sustainability
d) Sports education
Answer: c) Map-based learning of natural resources, environment and sustainability
Question 14. Where can students explore maps of India related to secondary stage learning?
a) https://bhuvan-app1.nrsc.gov.in/mhrd_ncert/
b) www.cbse.nic.in
c) www.isro.gov.in
d) www.ncert.nic.in
Answer: a) https://bhuvan-app1.nrsc.gov.in/mhrd_ncert/

