NCERT Economics Class 10 | How To Compare Different Countries or States?
Topic & sub-topics covered: How To Compare Different Countries or States?, Average Income: Development (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 10th about “How To Compare Different Countries or States?, Average Income” which is taken from the NCERT Economics for class 10th chapter no. 1 “Development“.
Download NCERT Economics Chapter 1 Class 10th Notes PDF for “Development”
Embark on a journey to understand the intricate dynamics of economic development with NCERT Economics Chapter 1 Class 10th Notes. Delving into the essence of “Development,” these notes offer a comprehensive overview of key concepts, theories, and real-world examples.
Download NCERT Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 Notes Development Economics Class 10 Chapter 1 Notes PDF
Available in PDF format, these notes provide a convenient and accessible resource for Class 10th students to enhance their understanding, facilitate revision, and excel in their studies. Download NCERT Economics Chapter 1 Class 10th Notes PDF now and unlock the keys to comprehending the dynamics of development in the global context.
How To Compare Different Countries or States?
1. Understanding Development Classification:
- Development can have diverse interpretations, leading to the categorization of countries as developed or underdeveloped.
2. Comparison Methodologies:
- Like comparing students based on various attributes, countries are compared using key characteristics such as income.
3. Importance of Income in Development:
- Income is a crucial determinant in comparing countries’ development levels, as it reflects the capacity to fulfill human needs and desires.
4. Concept of Total Income:
- The total income of a country is the collective income of all its residents, providing an overview of the country’s economic activity.
5. Challenges with Total Income Comparison:
- Comparing total income between countries is flawed due to differences in population sizes, as it doesn’t reflect the average income per person.
6. Introduction of Per Capita Income:
- Per capita income, calculated by dividing total income by total population, offers a more accurate measure for comparing individual prosperity across countries.
7. Role of Per Capita Income in Classification:
- The World Development Reports by the World Bank utilize per capita income to classify countries into different income categories, such as high-income and low-income countries.
8. Per Capita Income Classifications:
- High-income countries have a per capita income of US$ 49,300 per annum or more, while low-income countries have a per capita income of US$ 2500 or less.
9. India’s Income Classification:
- India falls within the category of low-middle-income countries due to its per capita income of US$ 6700 per annum in 2019.
Average Income
1. Understanding Averages in Comparison:
- Averages serve as a tool for comparing different entities, but they can mask underlying disparities.
2. Illustration with Two Countries:
- Using the example of countries A and B with five citizens each, the concept of average income is analyzed.
3. Calculation of Average Income:
- Students are tasked with calculating the average income for both countries based on the provided data in Table 1.2.
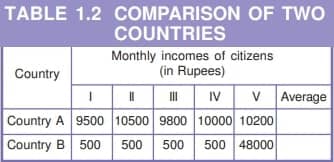
4. Consideration of Country Preference:
- Despite having identical average incomes, preferences for living in country A over country B may vary due to factors like equitable income distribution.
5. Importance of Income Distribution:
- While average income facilitates comparison, it fails to reflect how income is distributed among the population.
6. Equitable Distribution in Country A:
- Country A is favoured due to its more equitable income distribution, where individuals are neither excessively wealthy nor impoverished.
7. Disparity in Country B:
- Country B exhibits stark disparities, with most citizens being poor while one individual possesses extreme wealth.
8. Limitations of Average Income Comparison:
- The scenario highlights the limitation of relying solely on average income to gauge a country’s development, emphasizing the importance of income distribution.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Economics Class 10 Chapter 1: Development
FAQs
Q1. How are countries categorized in terms of development, and what factors influence these classifications?
Answer: Countries are categorized as developed or underdeveloped based on factors like income levels, infrastructure, education, and healthcare accessibility.
Q2. Why is income considered a crucial determinant in comparing countries’ development levels?
Answer: Income reflects the economic capacity to fulfil human needs and desires, making it a vital indicator for assessing development levels across countries.
Q3. How does per capita income classification influence global economic assessments, and what are the classifications used?
Answer: Per capita income classifications, such as high-income and low-income countries, are utilized in global economic assessments, with thresholds determining a country’s classification.

