NCERT Political Science Class 10 Chapter 5 Notes | Economic Growth And Development
Topic & sub-topics covered: “Economic Growth And Development” and MCQs Questions: Outcomes of Democracy (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 10th about “Economic Growth And Development” from the NCERT Political Science (Civics) notes for class 10th chapter 5 “Outcomes of Democracy“.
Download the NCERT Political Science (Civics) for Class 10 Chapter 5 Outcomes of Democracy PDF Notes
Download the NCERT Political Science (Civics) Class 10 Chapter 5 “Outcomes of Democracy” PDF Notes to revise key concepts quickly. This chapter explains how democracy affects a country’s governance, economy, social equality, and citizen rights. It discusses whether democratic systems meet people’s expectations by being accountable, inclusive, and respecting individual dignity. These notes offer a concise summary—perfect for exam prep or quick understanding.
Economic Growth And Development

1. Expectation of Development in Democracy:
- Democracies are expected to produce good governments and facilitate economic development.
- Evidence shows that many democracies fail to meet the expectation of high economic growth.
2. Comparison of Democracies and Dictatorships:
- Between 1950 and 2000, dictatorships had a slightly higher economic growth rate than democracies.
- This raises concerns about democracy’s ability to achieve higher economic development.
3. Economic Development: Factors Beyond Governance:
- Economic development depends on various factors:
a. The population size of the country.
b. The global situation and economic trends.
c. Cooperation from other countries.
d. The government sets economic priorities. -
Governance alone (democracy or dictatorship) does not guarantee economic success.
4. Negligible Difference in Less Developed Countries:
- The difference in economic growth rates between less developed countries under democracies and dictatorships is negligible.
- Democracy may not guarantee economic development, but it does not significantly lag behind dictatorship in this respect.
5. Preference for Democracy:
- Despite slower economic growth, democracy is preferred due to its positive outcomes:
a. Ensures accountability and transparency.
b. Provides freedom and representation to citizens.
c. Promotes human rights and dignity.
6. Conclusion:
- Democracy may not always excel in economic development, but its broader benefits outweigh the marginal advantage of dictatorship in growth rates.
Extra:
Economic Outcomes of Democracy
1. Importance of Arguments About Democracy:
- Discussions on democracy are passionate because they appeal to deep values.
- Some debates, like the economic outcomes of democracy, can be resolved using facts and figures.
2. Democracy vs. Dictatorship: Economic Growth:
- On average, dictatorial regimes show a slightly better economic growth record than democracies.
- However, in poor countries, the difference in economic growth between democracies and dictatorships is negligible.
3. Economic Inequalities in Democracies:
- Democracies exhibit a high degree of economic inequality.
- Examples:
a. South Africa and Brazil: The top 20% control more than 60% of national income, while the bottom 20% get less than 3%.
b. Denmark and Hungary: Show relatively better equality in income distribution.
4. Inequality of Opportunities:
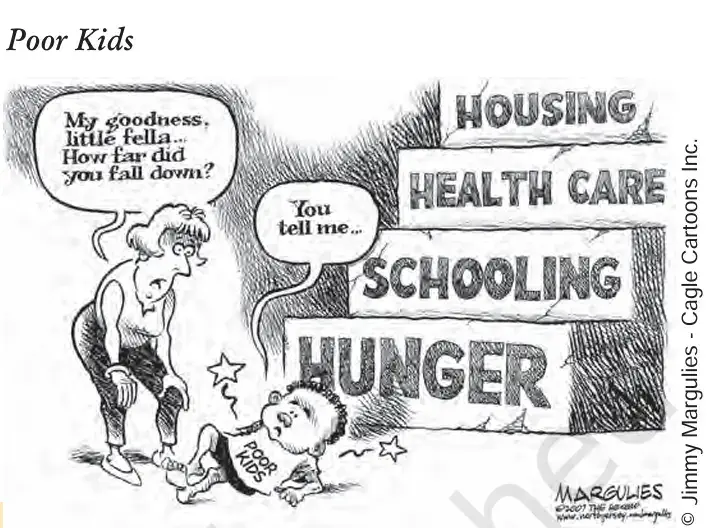
- The cartoon highlights the inequality of opportunities for the poorer sections in democratic societies.
- Poorer groups often face barriers despite the promises of equality in democracies.
5. Evidence-Based Analysis:
- Careful evidence from students of democracy reveals:
a. Economic growth does not consistently favour either democracy or dictatorship.
b. Inequalities persist within democracies, affecting income and opportunities.
6. Conclusion:
-
While democracies may not excel in economic equality, their broader values and ability to ensure freedom and representation make them preferable in the long run.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Political Science (Civics) Class 10 Chapter 5: Outcomes of Democracy
MCQs on NCERT Civics Class 10 Chapter 5 Topic – Economic Growth And Development
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Economic Growth and Development” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. What is a common expectation from democracies in terms of economic outcomes?
(a) They guarantee economic growth
(b) They ensure equitable income distribution
(c) They produce development
(d) They eliminate poverty completely
Answer: (c) They produce development
Question 2. How do dictatorships compare with democracies in terms of economic growth between 1950 and 2000?
(a) Democracies had a significantly higher growth rate
(b) Dictatorships had a slightly higher growth rate
(c) Democracies and dictatorships had equal growth rates
(d) Democracies completely outperformed dictatorships
Answer: (b) Dictatorships had a slightly higher growth rate
Question 3. What factors influence a country’s economic development, regardless of its form of government?
(a) Population size and economic priorities
(b) Cooperation from other countries
(c) Global situations
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Question 4. Why is the inability of democracy to achieve higher economic development not a reason to reject it?
(a) Economic growth is the only outcome of democracy
(b) Democracies are always lagging behind dictatorships
(c) Democracy has other positive outcomes besides economic growth
(d) Economic priorities do not matter in democracies
Answer: (c) Democracy has other positive outcomes besides economic growth
Question 5. What does evidence show about economic inequalities within democracies?
(a) Democracies eliminate economic inequalities
(b) Democracies have no economic inequalities
(c) Democracies can exhibit a high degree of economic inequalities
(d) Democracies ensure equality in income distribution
Answer: (c) Democracies can exhibit a high degree of economic inequalities
Question 6. Which countries are examples of high economic inequality within democracies?
(a) Denmark and Hungary
(b) South Africa and Brazil
(c) Canada and Australia
(d) France and Japan
Answer: (b) South Africa and Brazil
Question 7. In which countries do the top 20% of people take away more than 60% of the national income?
(a) Denmark and Hungary
(b) South Africa and Brazil
(c) USA and UK
(d) China and Russia
Answer: (b) South Africa and Brazil
Question 8. Which countries are examples of better income equality within democracies?
(a) Denmark and Hungary
(b) South Africa and Brazil
(c) India and China
(d) USA and Japan
Answer: (a) Denmark and Hungary
Question 9. What is depicted in the cartoon related to democracies and economic inequalities?
(a) Complete elimination of poverty
(b) Inequality of opportunities for poorer sections
(c) Equal opportunities for all
(d) Dictatorships having no economic inequalities
Answer: (b) Inequality of opportunities for poorer sections
Question 10. Why do some people prefer democracy despite its limitations in economic development?
(a) Democracies eliminate all economic challenges
(b) Democracies guarantee equality in income
(c) Democracies have several positive outcomes, like accountability and legitimacy
(d) Democracies do not rely on citizen participation
Answer: (c) Democracies have several positive outcomes, like accountability and legitimacy
Question 11. What does Table 1 show about economic growth in poor countries under different regimes?
(a) Democracies perform much better
(b) Dictatorships perform much better
(c) There is virtually no difference between democracies and dictatorships
(d) Democracies fail entirely
Answer: (c) There is virtually no difference between democracies and dictatorships
Question 12. What is a reasonable expectation from democracy in terms of economic development?
(a) It will always outperform dictatorships
(b) It will not lag behind dictatorships significantly
(c) It will eliminate all inequalities
(d) It will ensure the fastest growth
Answer: (b) It will not lag behind dictatorships significantly
Question 13. Which value of democracy is emphasised in debates about its economic outcomes?
(a) Speed in decision-making
(b) Complete elimination of corruption
(c) Commitment to deep values like equality and representation
(d) Absence of public participation
Answer: (c) Commitment to deep values like equality and representation
Question 14. What is one of the positive outcomes of democracy besides economic growth?
(a) Military strength
(b) Lack of public opinion
(c) Accountability and transparency in governance
(d) Inefficient government mechanisms
Answer: (c) Accountability and transparency in governance

