Types Of Vegetation – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: Types Of Vegetation and MCQs Questions: Natural Vegetation And Wildlife (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “Types Of Vegetation” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 9th chapter 5 “Natural Vegetation And Wildlife“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Notes PDF
Let’s be honest, remembering the details of Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife can feel overwhelming with all the forest types, seasonal changes, and animal species. That’s why I’ve put together these notes in a clear and simple format. You’ll find everything explained step by step – like how monsoon patterns shape vegetation or why certain wildlife is unique to specific regions. These notes aren’t just summaries, they’re designed to help you connect the concepts with real examples. You can also download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Notes PDF for quick revision anytime.
Types Of Vegetation
1. Major Types of Vegetation in India
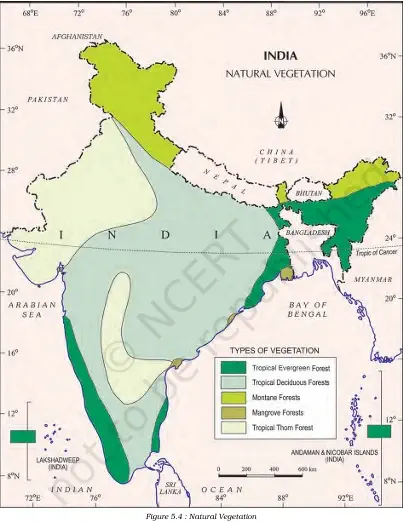
- India has five major types of natural vegetation.
- The classification is based on climatic conditions, soil type, and relief features.
- These vegetation types are:
I. Tropical Evergreen Forests
II. Tropical Deciduous Forests
III. Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
IV. Montane Forests
V. Mangrove Forests
I. Tropical Evergreen Forests
1. Distribution:
- Found in heavy rainfall areas.
- Major regions:
a. Western Ghats
b. Island groups – Lakshadweep, Andaman & Nicobar
c. Upper Assam
d. Tamil Nadu coast
2. Climatic Conditions:
- Grow in areas with more than 200 cm rainfall.
- Require short dry season.
- Region remains warm and wet throughout the year.
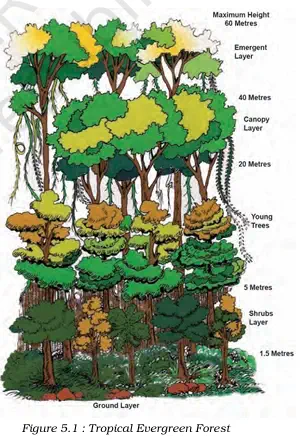
3. Vegetation Features:
- Tall trees up to 60 metres or more.
- Luxuriant vegetation – trees, shrubs, creepers.
- Multilayered structure.
- No definite shedding time – forests appear green all year round.
4. Commercially Important Trees:
- Ebony
- Mahogany
- Rosewood
- Rubber
- Cinchona
5. Wildlife:
- Common animals: elephant, monkey, lemur, deer.
- One-horned rhinoceroses: in Assam & West Bengal.
- Others: birds, bats, sloth, scorpions, snails.
Very Short Answer (1 mark)
Question: Tropical evergreen forests are found in regions with how much rainfall?
Answer: More than 200 cm.
Question: Name one commercial tree found in tropical evergreen forests.
Answer: Ebony/Mahogany/Rosewood (any one).
Question: Why do tropical evergreen forests remain green throughout the year?
Answer: Because trees do not shed leaves at a definite time.
Short Answer (3 marks)
Question: Write three features of tropical evergreen forests.
Answer: Three features of tropical evergreen forests:
- Found in areas with more than 200 cm rainfall.
- Tall trees (up to 60 metres), multilayered structure.
- Remain green throughout the year as there is no fixed shedding period.
Question: Name any four animals found in tropical evergreen forests.
Answer: Elephant, monkey, lemur, deer (others may include rhinoceros, sloth, bats).
II. Tropical Deciduous Forests

1. General Features:
- Most widespread forests of India.
- Also called Monsoon Forests.
- Grow in areas receiving 70 cm – 200 cm rainfall.
- Trees shed leaves for 6–8 weeks in dry summer.
2. Sub-types (based on rainfall / water availability):
A. Moist Deciduous Forests:
- Rainfall: 200 – 100 cm.
- Distribution:
a. Northeastern states
b. Foothills of the Himalaya’s
c. Jharkhand
d. West Odisha & Chhattisgarh
e. Eastern slopes of Western Ghats - Dominant species: Teak.
- Other important species: Bamboo, Sal, Shisham, Sandalwood, Khair, Kusum, Arjun, Mulberry.
B. Dry Deciduous Forests:
- Rainfall: 100 – 70 cm.
- Distribution:
a. Rainier parts of Peninsular Plateau
b. Plains of Bihar & Uttar Pradesh - Vegetation: Open stretches – Teak, Sal, Peepal, Neem.
- Human use: Large parts cleared for cultivation & grazing.
3. Wildlife:
- Common animals: Lion, Tiger, Pig, Deer, Elephant.
- Other fauna: Birds, Lizards, Snakes, Tortoises.
Very Short Answer (1 mark)
Question: Which is the most widespread forest type in India?
Answer: Tropical Deciduous Forests.
Question: Another name for Tropical Deciduous Forests?
Answer: Monsoon Forests.
Question: Trees of tropical deciduous forests shed leaves for how many weeks?
Answer: 6–8 weeks in dry summer.
III. The Thorn Forests and Scrubs
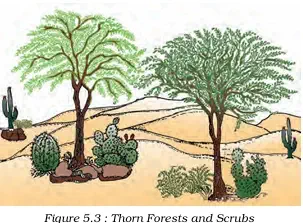
1. General Features:
- Found in regions with less than 70 cm rainfall.
- Natural vegetation – thorny trees and bushes.
2. Distribution:
- North-Western India and semi-arid areas:
a. Gujarat
b. Rajasthan
c. Madhya Pradesh
d. Chhattisgarh
e. Uttar Pradesh
f. Haryana
3. Vegetation:
- Major plant species: Acacias, Palms, Euphorbias, Cacti.
- Scattered trees with adaptations:
a. Long roots – penetrate deep to absorb moisture.
b. Succulent stems – store water.
c. Small/thick leaves – reduce evaporation. - In arid areas – vegetation changes into scrubs and thorn forests.
4. Wildlife:
- Common animals:
a. Small mammals: rats, mice, rabbits
b. Carnivores: fox, wolf, tiger, lion
c. Herbivores/transport animals: wild ass, horses, camels
Very Short Answer (1 mark)
Question: Thorn forests are found in areas receiving less than how much rainfall?
Answer: 70 cm.
Question: Name two states where thorn forests are found.
Answer: Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Question:: Give two examples of plants found in thorn forests.
Answer: Acacia, Cactus.
IV. Montane Forests
1. General Characteristics:
- Found in mountainous areas.
- Temperature decreases with altitude – leads to change in natural vegetation.
- Vegetation succession: tropical – temperate – alpine – tundra (altitude belts).
2. Vegetation by Altitude:
- 1000–2000 m (Wet Temperate Forests)
a. Dominant trees: Evergreen broad-leaf trees (oak, chestnut). - 1500–3000 m (Temperate Coniferous Forests)
a. Trees: Pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce, cedar.
b. Distribution: Southern slopes of Himalayas, high-altitude areas of Southern & North-Eastern India. - Above 3600 m (Alpine Vegetation)
a. Trees: Silver fir, juniper, pine, birch.
b. Features: Trees become stunted near snowline.
c. Alpine grasslands – used by nomadic tribes (Gujjars, Bakarwals) for grazing. - Higher Altitudes (Tundra Type)
a. Vegetation: Mosses, lichens.
3. Animal Life:
- Common species:
a. Large mammals: Kashmir stag, wild sheep, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, bear, red panda, ibex.
b. Smaller animals: Spotted deer, jack rabbit, squirrel.
c. Domestic animals adapted: Sheep and goats with thick hair.
Very Short Answer (1 mark)
Question: At what height are wet temperate forests found?
Answer: 1000–2000 metres.
Question: Name two trees found in coniferous forests of montane regions.
Answer: Pine, Deodar.
Question: Which nomadic tribes use Alpine grasslands for grazing?
Answer: Gujjars and Bakarwals.
V. Mangrove Forests
1. General Features:
- Found in coastal areas influenced by tides.
- Formed where mud and silt get accumulated on coasts.
- Roots of plants are submerged under water – special adaptation.
- Vegetation is dense mangroves.
2. Distribution (Delta Regions):
- Major deltas covered by mangroves:
a. Ganga
b. Mahanadi
c. Krishna
d. Godavari
e. Kaveri - Ganga-Brahmaputra delta – Sundari trees (provide durable, hard timber).
3. Important Trees:
- Sundari (most important, hard timber).
- Palm
- Coconut
- Keora
- Agar
4. Animal Life:
- Royal Bengal Tiger (most famous).
- Turtles
- Crocodiles
- Gharials
- Snakes
Very Short Answer (1 mark)
Question: Where are mangrove tidal forests found?
Answer: In coastal areas influenced by tides, with mud and silt deposits.
Question: Name the famous animal found in mangrove forests.
Answer: Royal Bengal Tiger.
Question: What is the use of Sundari trees?
Answer: Provide durable, hard timber.
Medicinal Plants
1. General Facts:
- India is famous for herbs and spices since ancient times.
- Ayurveda describes about 2,000 plants.
- 500 plants are in regular use.
- IUCN (World Conservation Union) Red List:
a. Total medicinal plants named: 352
b. Critically threatened: 52
c. Endangered: 49
2. Commonly Used Medicinal Plants in India:
- Sarpagandha:
a. Found only in India.
b. Used to treat blood pressure. - Jamun:
a. Ripe fruit juice – vinegar (carminative, diuretic, aids digestion).
b. Seed powder – controls diabetes. - Arjun:
a. Fresh leaf juice – cures earache.
b. Also used to regulate blood pressure. - Babool:
a. Leaves – cure eye sores.
b. Gum – used as a tonic. - Neem: Has strong antibiotic and antibacterial properties.
- Tulsi: Used to cure cough and cold.
- Kachnar:
a. Used to cure asthma and ulcers.
b. Buds and roots – good for digestive problems.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Geography Class 9 Chapter 5: Natural Vegetation And Wildlife
| Topics No. | Topics Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Types Of Vegetation |
| 2 | Wildlife |
MCQs on NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 5 Topic – Types Of Vegetation
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Types Of Vegetation” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. How many major types of vegetation are found in India?
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
d) 6
Answer: c) 5
Question 2. Which of the following is not a major type of vegetation in India?
a) Tropical Evergreen Forests
b) Desert Grasslands
c) Montane Forests
d) Mangrove Forests
Answer: b) Desert Grasslands
Question 3. Tropical evergreen forests are best developed in regions receiving more than:
a) 100 cm rainfall
b) 150 cm rainfall
c) 200 cm rainfall
d) 250 cm rainfall
Answer: c) 200 cm rainfall
Question 4. Which of the following states/regions have tropical evergreen forests?
a) Western Ghats, Andaman & Nicobar, Assam, Tamil Nadu coast
b) Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana
c) Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim
d) Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh
Answer: a) Western Ghats, Andaman & Nicobar, Assam, Tamil Nadu coast
Question 5. Trees of tropical evergreen forests can reach a height of:
a) 30 m
b) 40 m
c) 50 m
d) 60 m or more
Answer: d) 60 m or more
Question 6. Which of the following trees belong to tropical evergreen forests?
a) Teak and Sal
b) Ebony, Mahogany, Rosewood, Rubber, Cinchona
c) Acacia and Cactus
d) Oak and Pine
Answer: b) Ebony, Mahogany, Rosewood, Rubber, Cinchona
Question 7. One-horned rhinoceros are found in:
a) Western Ghats
b) Assam and West Bengal
c) Tamil Nadu coast
d) Lakshadweep Islands
Answer: b) Assam and West Bengal
Question 8. Which type of forests are the most widespread in India?
a) Tropical Evergreen
b) Tropical Deciduous
c) Montane Forests
d) Mangrove Forests
Answer: b) Tropical Deciduous
Question 9. Tropical deciduous forests are also called:
a) Monsoon forests
b) Rain forests
c) Dry forests
d) Alpine forests
Answer: a) Monsoon forests
Question 10. Rainfall range for tropical deciduous forests is:
a) 200 cm and above
b) 200 cm – 70 cm
c) Less than 70 cm
d) 50 cm – 150 cm
Answer: b) 200 cm – 70 cm
Question 11. Trees of deciduous forests shed leaves for how many weeks in summer?
a) 2–3 weeks
b) 4–5 weeks
c) 6–8 weeks
d) 10–12 weeks
Answer: c) 6–8 weeks
Question 12. Moist deciduous forests are found in:
a) Eastern slopes of Western Ghats
b) Rajasthan and Gujarat
c) Himachal Pradesh
d) Punjab and Haryana
Answer: a) Eastern slopes of Western Ghats
Question 13. Which is the most dominant species of tropical deciduous forests?
a) Sal
b) Teak
c) Neem
d) Sandalwood
Answer: b) Teak
Question 14. Dry deciduous forests are found in:
a) Eastern Himalayas
b) Plains of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh
c) Lakshadweep Islands
d) Kerala coast
Answer: b) Plains of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh
Question 15. Thorn forests are found in regions with rainfall:
a) More than 200 cm
b) Between 200–70 cm
c) Less than 70 cm
d) Between 100–70 cm
Answer: c) Less than 70 cm
Question 16. Thorn forests are commonly found in:
a) Kerala, Tamil Nadu
b) Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana
c) Assam, Meghalaya
d) Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand
Answer: b) Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana
Question 17. Which feature helps plants survive in thorn forests?
a) Soft stems and broad leaves
b) Long roots, thick stems, small leaves
c) Needle-shaped leaves
d) Large crowns and evergreen foliage
Answer: b) Long roots, thick stems, small leaves
Question 18. Common animals in thorn forests are:
a) Elephants and Rhinoceroses
b) Lions, Camels, Wild Ass, Foxes
c) Yaks and Red Panda
d) Royal Bengal Tigers and Crocodiles
Answer: b) Lions, Camels, Wild Ass, Foxes
Question 19. Which type of vegetation is found in mountains due to decreasing temperature with altitude?
a) Desert vegetation
b) Montane forests
c) Evergreen forests
d) Mangroves
Answer: b) Montane forests
Question 20. Wet temperate forests are found at heights between:
a) 500–1000 m
b) 1000–2000 m
c) 2000–3000 m
d) Above 3600 m
Answer: b) 1000–2000 m
Question 21. Coniferous trees like pine, deodar, fir and spruce are found between:
a) 500–1000 m
b) 1000–2000 m
c) 1500–3000 m
d) 3600 m and above
Answer: c) 1500–3000 m
Question 22. Alpine vegetation occurs above:
a) 1000 m
b) 2000 m
c) 3000 m
d) 3600 m
Answer: d) 3600 m
Question 23. Which nomadic tribes graze their animals on Alpine grasslands?
a) Gujjars and Bakarwals
b) Bhils and Gonds
c) Todas and Nicobarese
d) Santhals and Nagas
Answer: a) Gujjars and Bakarwals
Question 24. Which rare animal is found in montane forests?
a) Royal Bengal Tiger
b) Red Panda
c) Camel
d) Wild Ass
Answer: b) Red Panda
Question 25. Mangrove forests are found in:
a) Himalayas
b) Coastal areas influenced by tides
c) Western Ghats
d) Rajasthan Desert
Answer: b) Coastal areas influenced by tides
Question 26. Sundari trees, providing hard timber, are found in:
a) Sundarbans (Ganga–Brahmaputra delta)
b) Western Ghats
c) Nilgiris
d) Thar Desert
Answer: a) Sundarbans (Ganga–Brahmaputra delta)
Question 27. Which animal is most famous in mangrove forests?
a) Red Panda
b) Royal Bengal Tiger
c) Yak
d) Wild Ass
Answer: b) Royal Bengal Tiger
Question 28. How many plants are described in Ayurveda?
a) 500
b) 1000
c) 2000
d) 3000
Answer: c) 2000
Question 29. How many medicinal plants are in regular use in India?
a) 200
b) 300
c) 400
d) 500
Answer: d) 500
Question 30. How many medicinal plants are critically threatened according to the Red List?
a) 49
b) 52
c) 60
d) 70
Answer: b) 52
Question 31. Sarpagandha is used for treating:
a) Diabetes
b) Blood pressure
c) Cough and cold
d) Ulcers
Answer: b) Blood pressure
Question 32. Jamun seeds are useful in controlling:
a) Asthma
b) Diabetes
c) Blood pressure
d) Earache
Answer: b) Diabetes
Question 33. Which plant’s juice of leaves is used to cure earache?
a) Neem
b) Arjun
c) Babool
d) Tulsi
Answer: b) Arjun
Question 34. Babool leaves are used to cure:
a) Diabetes
b) Asthma
c) Eye sores
d) Cough and cold
Answer: c) Eye sores
Question 35. Neem is known for its:
a) Antibiotic and antibacterial properties
b) Earache treatment
c) Diabetes cure
d) Asthma cure
Answer: a) Antibiotic and antibacterial properties
Question 36. Tulsi is mainly used to cure:
a) Blood pressure
b) Cough and cold
c) Ulcers
d) Eye sores
Answer: b) Cough and cold
Question 37. Kachnar is useful in treating:
a) Asthma and ulcers
b) Diabetes and hypertension
c) Cough and cold
d) Eye sores and fever
Answer: a) Asthma and ulcers