Distribution Of Rainfall – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: Distribution Of Rainfall and MCQs Questions: Climate (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “Distribution Of Rainfall” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 9th chapter 4 “Climate“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 4 Climate Notes PDF
NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 4 – Climate Notes & MCQ’s Question-Answer – E-book NCERT
The Climate chapter of Class 9 Geography explores the factors that influence India’s diverse weather patterns. These notes explain major elements like temperature, rainfall, pressure, and wind systems, along with concepts such as monsoons, seasons, factors that affect climate and climatic controls. Students will also find clear points on why different regions in India experience varied climates and how these patterns affect daily life and agriculture. The PDF is designed to make revision easy with concise summaries, diagrams, and exam-ready pointers. Download the NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 4 Climate Notes PDF to prepare effectively and build a solid understanding of this topic.
Distribution Of Rainfall
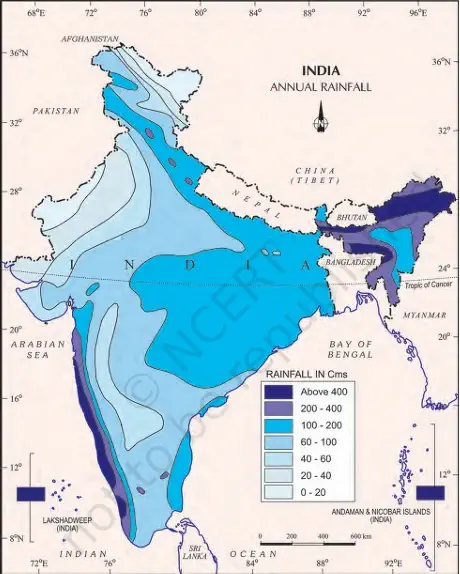
1. High Rainfall Areas:
- Western coast and Northeastern India receive over 400 cm of rainfall annually.
- Example: Mawsynram and Cherrapunji (world’s wettest places).
2. Low Rainfall Areas:
- Less than 60 cm of rainfall in:
a. Western Rajasthan
b. Parts of Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab - Rainfall also low in:
a. Interior Deccan Plateau
b. East of the Sahyadris (rain-shadow region). - Leh (Jammu & Kashmir) is another area of very low precipitation.
3. Moderate Rainfall Areas:
- Most of the country receives moderate rainfall (between 60–200 cm).
4. Snowfall:
- Restricted only to Himalayan region.
5. Variability of Rainfall:
- Rainfall is highly variable year to year due to monsoon nature.
- Variability is highest in low rainfall regions (Rajasthan, Gujarat, leeward side of Western Ghats).
6. Impact of Uneven Distribution:
- High rainfall areas – Flood-prone.
- Low rainfall areas – Drought-prone.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Geography Class 9 Chapter 4: Climate
| Topics No. | Topics Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Climatic Controls |
| 2 | Factors Affecting India’s Climate |
| 3 | The Seasons |
| 4 | Distribution Of Rainfall |
| 5 | Monsoon As A Unifying Bond |
MCQs on NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 4 Topic – Distribution Of Rainfall
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Distribution Of Rainfall” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. Which regions of India receive over 400 cm of rainfall annually?
a) Western Rajasthan and Gujarat
b) Parts of western coast and northeastern India
c) Leh and Ladakh
d) Punjab and Haryana
Answer: b) Parts of western coast and northeastern India
Question 2. Which regions of India receive less than 60 cm of rainfall annually?
a) Northeastern states
b) Western Rajasthan, adjoining Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab
c) Western coast
d) Deccan Plateau
Answer: b) Western Rajasthan, adjoining Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab
Question 3. In which region of Jammu and Kashmir is rainfall very low?
a) Srinagar
b) Leh
c) Jammu
d) Pulwama
Answer: b) Leh
Question 4. Snowfall in India is mainly restricted to:
a) Deccan Plateau
b) Coastal areas
c) Himalayan region
d) Desert regions
Answer: c) Himalayan region
Question 5. Why does the interior of the Deccan plateau receive low rainfall?
a) Because it lies in the rain shadow region of the Western Ghats
b) Because it is close to the sea
c) Because it receives snowfall instead
d) Because it is a desert region
Answer: a) Because it lies in the rain shadow region of the Western Ghats
Question 6. Which side of the Sahyadris receives low rainfall?
a) Windward side
b) Coastal side
c) Eastern leeward side
d) Western slopes
Answer: c) Eastern leeward side
Question 7. Why is rainfall highly variable in India?
a) Because monsoons are uncertain and irregular
b) Because snowfall affects rainfall
c) Because India is close to the equator
d) Because of proximity to oceans
Answer: a) Because monsoons are uncertain and irregular
Question 8. Areas of high rainfall in India are more likely to face:
a) Earthquakes
b) Droughts
c) Floods
d) Landslides only
Answer: c) Floods
Question 9. Areas of low rainfall in India are more likely to be:
a) Drought-prone
b) Flood-prone
c) Cyclone-prone
d) Snowfall-prone
Answer: a) Drought-prone
Question 10. Which regions show high variability of rainfall in India?
a) Western Rajasthan, Gujarat, and leeward side of Western Ghats
b) Northeastern states
c) Coastal Kerala
d) Himalayan region
Answer: a) Western Rajasthan, Gujarat, and leeward side of Western Ghats