India And The World – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: India And The World and MCQs Questions: India – Size And Location (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “India And The World” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 9th chapter 1 “India – Size And Location“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 1 India – Size And Location Notes PDF
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 1 India – Size And Location Notes PDF for a concise, students-first summary of this foundational unit. It explains latitude and longitude, India’s continental position, extent, and neighbors with simple maps and memorable examples. Use the one-page checklist to memories coordinates, standard meridian, and border facts.
Short diagrams clarify scale and distance problems, and quick practice questions mirror board patterns. Perfect for last-minute revision or classroom recap, the PDF helps you understand why India’s size and location matter for climate, transport, and strategy – without unnecessary fluff. Download it and revise confidently.
India And The World
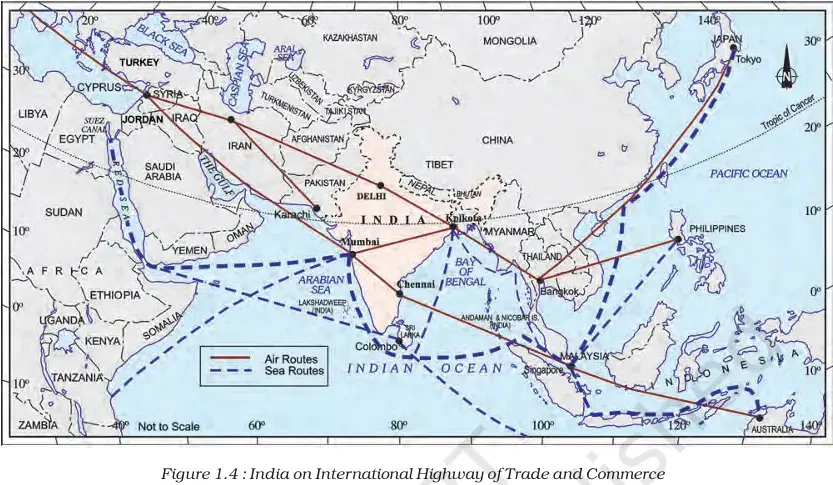
1. Strategic Location:
- India has a central location between East and West Asia.
- It is a southward extension of the Asian continent.
- The trans-Indian Ocean routes link:
a. Europe in the West
b. East Asia in the East
c. Giving India a strategic central location. - The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, helping India establish close contact:
a. From the western coast – West Asia, Africa, Europe.
b. From the eastern coast – Southeast and East Asia. - India has the longest coastline on the Indian Ocean.
- India’s eminent position in the Indian Ocean justifies the naming of the ocean after India.
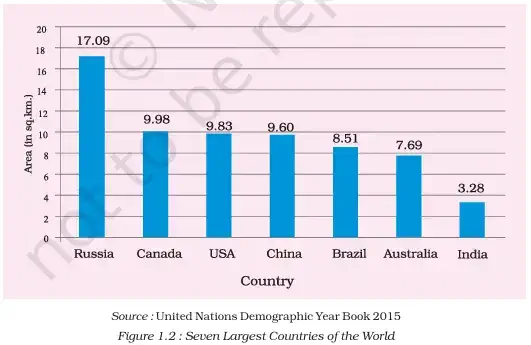
2. Historical Contacts:
- India’s land route contacts are much older than maritime contacts.
- Mountain passes in the north provided passages to ancient travellers.
- Oceans restricted interactions for a long time.
3. Cultural & Commercial Exchange:
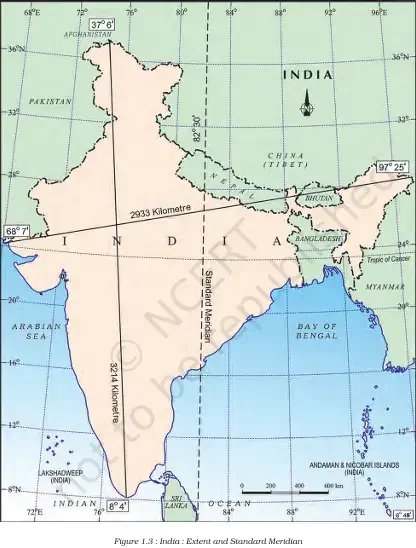
- Ideas spread from India to the world:
a. Upanishads
b. Ramayana
c. Panchatantra stories
d. Indian numerals & the decimal system - Commodities from India exported:
a. Spices
b. Muslin
c. Other merchandise - Foreign influence on India:
a. Greek sculpture
b. West Asian architecture – dome & minarets
4. Modern Development:
- Opening of Suez Canal (1869): Reduced India’s distance from Europe by 7,000 km.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Geography Class 9 Chapter 1: India – Size And Location
| Topics No. | Topics Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Location |
| 2 | Size |
| 3 | India And The World |
| 4 | India’s Neighbours |
MCQs on NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 1 Topic – India And The World
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “India And The World” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. The Indian landmass has a central location between which two regions?
a) Europe and Africa
b) East and West Asia
c) North and South America
d) Australia and Africa
Answer: b) East and West Asia
Question 2. India is a ______ extension of the Asian continent.
a) Northward
b) Southward
c) Eastward
d) Westward
Answer: b) Southward
Question 3. Which ocean routes provide India with a strategic central location?
a) Pacific Ocean routes
b) Atlantic Ocean routes
c) Trans Indian Ocean routes
d) Arctic Ocean routes
Answer: c) Trans Indian Ocean routes
Question 4. Which continents are connected through the trans-Indian Ocean routes?
a) Europe and Africa
b) Europe and East Asia
c) Africa and North America
d) Asia and Australia
Answer: b) Europe and East Asia
Question 5. Which physical feature of India helps establish close contacts with West Asia, Africa, and Europe?
a) Northern Plains
b) Deccan Peninsula
c) Himalayas
d) Thar Desert
Answer: b) Deccan Peninsula
Question 6. From which coast does India maintain close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe?
a) Eastern coast
b) Western coast
c) Southern coast
d) Northern coast
Answer: b) Western coast
Question 7. From which coast does India maintain close contact with Southeast and East Asia?
a) Western coast
b) Eastern coast
c) Northern coast
d) Southern coast
Answer: b) Eastern coast
Question 8. Why is the Indian Ocean named after India?
a) Because of India’s large population
b) Because India has the longest coastline on it
c) Because of India’s strong navy
d) Because India is the oldest civilization
Answer: b) Because India has the longest coastline on it
Question 9. Which type of contacts of India are much older than her maritime contacts?
a) Air route contacts
b) Land route contacts
c) River route contacts
d) Desert route contacts
Answer: b) Land route contacts
Question 10. Which provided passages to ancient travelers into India?
a) Deserts
b) Passes across northern mountains
c) Oceans
d) Rivers
Answer: b) Passes across northern mountains
Question 11. Which restricted India’s interaction with the world for a long time?
a) Rivers
b) Plateaus
c) Oceans
d) Forests
Answer: c) Oceans
Question 12. Which ideas and texts spread to many parts of the world through India’s land routes?
a) Vedas and Quran
b) Upanishads and Ramayana
c) Bible and Torah
d) Mahabharata and Gita only
Answer: b) Upanishads and Ramayana
Question 13. Which Indian stories reached other parts of the world?
a) Jataka tales
b) Panchtantra
c) Hitopadesha
d) Kathasaritsagara
Answer: b) Panchtantra
Question 14. Which mathematical concepts spread from India to the world?
a) Geometry and Algebra
b) Indian numerals and Decimal system
c) Trigonometry and Calculus
d) Fractions and Ratios
Answer: b) Indian numerals and Decimal system
Question 15. Which commodities were exported from India in ancient times?
a) Tea and Coffee
b) Spices, Muslin, and other merchandise
c) Silk and Porcelain
d) Cotton and Opium
Answer: b) Spices, Muslin, and other merchandise
Question 16. From which region did Greek sculpture influence India?
a) East Asia
b) West Asia
c) Europe
d) Central Asia
Answer: c) Europe
Question 17. The architectural styles of dome and minarets in India came from:
a) Central Asia
b) East Asia
c) West Asia
d) South-East Asia
Answer: c) West Asia
Question 18. When was the Suez Canal opened?
a) 1857
b) 1869
c) 1872
d) 1885
Answer: b) 1869
Question 19. The opening of the Suez Canal reduced India’s distance from Europe by:
a) 5,000 km
b) 6,000 km
c) 7,000 km
d) 8,000 km
Answer: c) 7,000 km

