Mesopotamia And Its Geography Class 11 – Concept, MCQs & Notes PDF
Topic covered: Mesopotamia and Its Geography class 11 notes and MCQs questions: Writing and City Life (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 11th about the “Mesopotamia and Its Geography“ from the NCERT history notes for class 11th chapter 1 Writing and City Life.
Download the NCERT History for Class 11th Chapter 1 Writing and City Life Notes PDF
Chapter 1 of Class 11 History, Writing and City Life, takes you into the early world of Mesopotamia, where writing first appeared and cities began to shape human life in new ways. Students often find the connection between trade, administration, and the development of writing a bit overwhelming, so these notes break everything into clear, story-like sections. You’ll understand how cities grew, why records became essential, and how everyday life looked in the earliest civilisations. If you want a simple, exam-friendly guide, you can download the NCERT History for Class 11th Chapter 1 Writing and City Life Notes PDF and revise with ease.
Mesopotamia And Its Geography
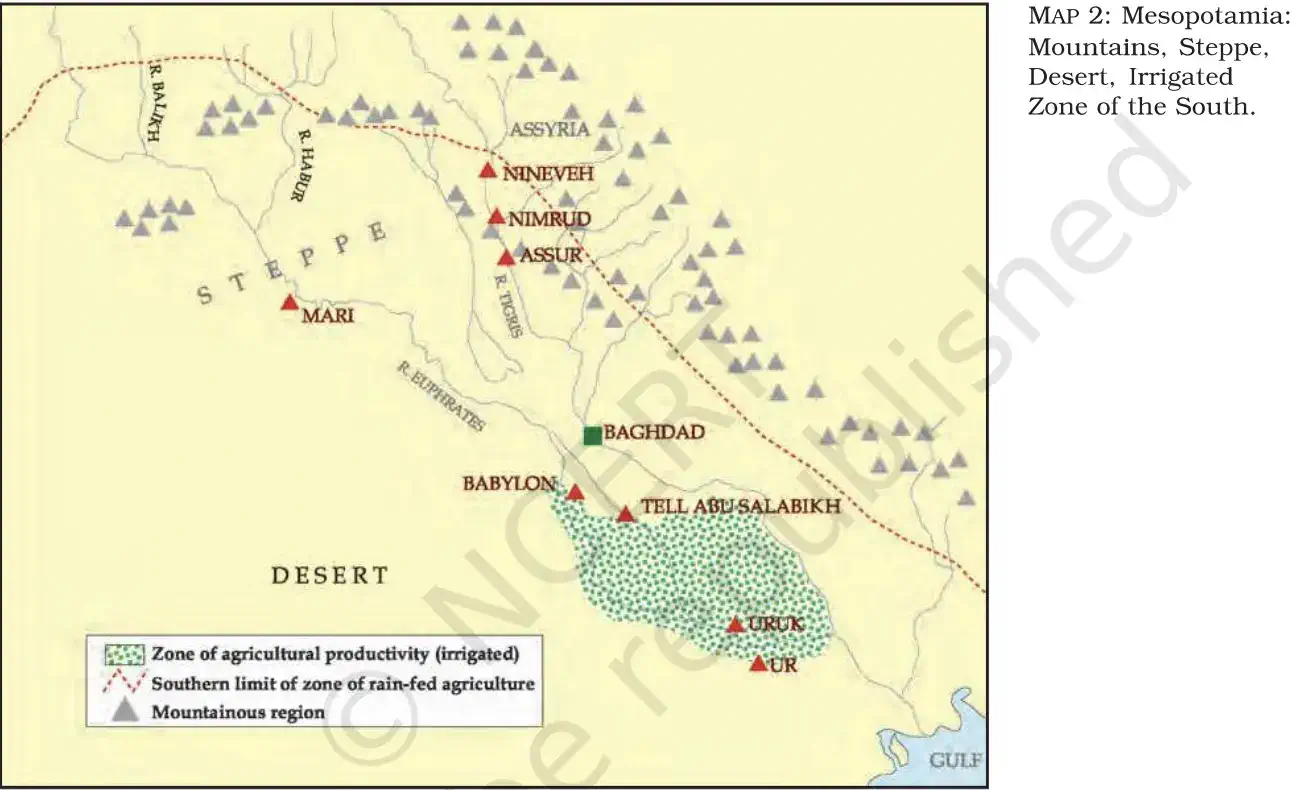
1. Diverse Environments of Iraq:
- Iraq has varied geographical features — mountains, plains, steppe, rivers, and desert.
- North-east: Green, undulating plains rising to tree-covered mountain ranges with clear streams and wildflowers.
- The region had sufficient rainfall for agriculture; farming began here between 7000–6000 BCE.
2. The Steppe Region:
- Located in the north, this upland area is called a steppe.
- Animal herding (sheep and goats) was more suitable than farming.
- Herds grazed on grasses and low shrubs that grew after winter rains.
3. Communication Routes and Neighbouring Regions:
- East of Mesopotamia: Tributaries of the Tigris River connected the plains to the mountains of Iran, serving as routes of communication and trade.
4. Southern Desert and Birth of Civilisation:
- The southern part of Mesopotamia was a desert, yet the first cities and writing emerged there.
- This was possible due to the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, which carried silt (fine mud) from the northern mountains.
- Flooding or irrigation deposited fertile silt, making agriculture possible in the desert.
5. Irrigation and Agriculture:
- After entering the desert, the Euphrates divided into small channels.
- These channels acted as natural irrigation canals, flooding banks and watering crops like wheat, barley, peas, and lentils.
- The southern Mesopotamian agriculture was among the most productive in the ancient world, even more efficient than Roman agriculture later.
6. Livestock and Other Resources:
- Sheep and goats from the steppe, plains, and mountain slopes provided meat, milk, and wool in large quantities.
- Fish were abundant in rivers.
- Date palms supplied fruit during the summer, adding to the food diversity.
7. Beyond Rural Prosperity:
- Prosperous agriculture and livestock alone did not lead to city growth.
- The rise of Mesopotamian cities involved other social, economic, and political factors, discussed later in the chapter.
Summary of “Mesopotamia and Its Geography Class 11”
Mesopotamia grew out of a landscape that shifted from green plains in the northeast to dry desert in the south. Farming began early in the rain-fed northern zones, while the steppe supported herding. The real turning point came in the southern desert, where the Tigris and Euphrates spread fertile silt across the land. Their floodwaters fed a dense network of channels that made wheat, barley, peas, and lentils possible even without rainfall. Herding, fishing, and date-palms added to the region’s resources. This mix of fertile river plains and abundant livestock set the stage for the rise of early cities and writing.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE History Class 11 Chapter 1: Writing and City Life
MCQs on NCERT History Class 11 Chapter 1 Topic – Mesopotamia and Its Geography Class 11 Notes
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Mesopotamia and Its Geography Class 11 Notes” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. The earliest agriculture in north-east Mesopotamia began around
a) 9000–8000 BCE
b) 8000–7000 BCE
c) 7000–6000 BCE
d) 6000–5000 BCE
Answer: c)
Question 2. Which region of Mesopotamia had tree-covered mountains, clear streams and enough rainfall for crops?
a) Northern steppe
b) North-east
c) Southern desert
d) Western plateau
Answer: b)
Question 3. The northern upland region suitable mainly for herding is known as
a) Oasis
b) Steppe
c) Plateau
d) Basin
Answer: b)
Question 4. Which animals grazed on the northern steppe after winter rains?
a) Cows and buffaloes
b) Horses and donkeys
c) Sheep and goats
d) Camels and oxen
Answer: c)
Question 5. Which natural feature connected Mesopotamia with the mountains of Iran?
a) Euphrates canals
b) Desert routes
c) Tigris tributaries
d) Coastal paths
Answer: c)
Question 6. The first cities of Mesopotamia developed in
a) North-east plains
b) Northern steppe
c) Southern desert
d) Eastern mountains
Answer: c)
Question 7. The southern desert could support cities mainly because
a) It received heavy rainfall
b) It had natural lakes
c) Euphrates and Tigris brought fertile silt
d) It had many trade routes
Answer: c)
Question 8. Which rivers carried silt that made Mesopotamian agriculture productive?
a) Nile and Jordan
b) Indus and Sutlej
c) Tigris and Shatt-al-Arab
d) Tigris and Euphrates
Answer: d)
Question 9. When Euphrates entered the desert, it broke into
a) Deep wells
b) Natural lakes
c) Small channels
d) Rocky streams
Answer: c)
Question 10. These small channels in southern Mesopotamia mainly functioned as
a) Trade routes
b) Irrigation canals
c) Fishing zones
d) Defensive trenches
Answer: b)
Question 11. The main crops of southern Mesopotamia included
a) Rice and millet
b) Wheat, barley, peas, lentils
c) Maize and sugarcane
d) Cotton and jute
Answer: b)
Question 12. Which ancient region had the most productive agriculture among all early systems mentioned?
a) Roman Empire
b) Egypt
c) Indus Valley
d) Southern Mesopotamia
Answer: d)
Question 13. Why was the agriculture of southern Mesopotamia impressive despite low rainfall?
a) Underground water reserves
b) Imported food
c) Fertile silt and irrigation canals
d) Use of metal tools
Answer: c)
Question 14. Sheep and goats of Mesopotamia provided all except
a) Meat
b) Milk
c) Wool
d) Silk
Answer: d)
Question 15. Which food source was easily available in Mesopotamian rivers?
a) Fish
b) Rice
c) Cotton
d) Spices
Answer: a)
Question 16. Date-palms in Mesopotamia mainly gave
a) Oil
b) Timber
c) Fruit in summer
d) Fibre for cloth
Answer: c)
Question 17. The paragraph warns not to assume that cities grew only because of
a) Trade
b) Rural prosperity
c) River transport
d) Natural resources
Answer: b)
Question 18. Agriculture began earliest in which part of Iraq?
a) Southern desert
b) Eastern mountains
c) North-east plains
d) Central plateau
Answer: c)
Question 19. The region too high for rivers to fertilise was
a) Desert
b) Mountains and steppe
c) River basin
d) Canal network
Answer: b)
Question 20. The steppe region is most suitable for
a) Mining
b) Fishing
c) Herding
d) Metalwork
Answer: c)

