NCERT Geography Class 10 | Importance Of Manufacturing
Topic & sub-topics covered: Importance Of Manufacturing and MCQs Questions: Minerals and Energy Resources (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 10th about the “Importance Of Manufacturing” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 10th chapter 6th “Manufacturing Industries“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 10th Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries PDF Notes
Chapter 6 of NCERT Geography for Class 10, “Manufacturing Industries”, delves into the backbone of India’s economy by highlighting the role of manufacturing in economic development, industrial types, their distribution, and environmental impacts. These PDF notes are essential for Class 10 students aiming to excel in board exams, as they simplify complex concepts and include exam-focused content.
Our notes are curated by experts and tailored for CBSE students. These PDF notes cover every aspect of Manufacturing Industries while focusing on scoring high in exams. Visit eBook NCERT to download Chapter 6: Manufacturing Industries PDF Notes for Class 10 Geography. These notes are designed to simplify learning and enhance retention for exam success. Start your preparation today and get a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing industries in India!
Importance Of Manufacturing
1. Role of Manufacturing Sector in Development
- Manufacturing is the backbone of general and economic development.
- Key contributions of manufacturing industries:
a. Modernizes agriculture, reducing dependence on agricultural income.
b. Provides jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. - Industrial development helps:
a. Eradicate unemployment and poverty.
b. Reduce regional disparities by setting up industries in tribal and backward areas. - Export of manufactured goods:
a. Expand trade and commerce.
b. Brings in foreign exchange. - The prosperity of nations depends on transforming raw materials into high-value finished goods.
2. Interdependence of Agriculture and Industry:
- Agriculture and industry are interdependent:
a. Agro-industries boost agricultural productivity.
b. Industries provide farmers with products like irrigation pumps, fertilizers, insecticides, and tools. - The manufacturing industry enhances agricultural efficiency and productivity.
3. Global Competitiveness in Manufacturing:
- Industries must be efficient and competitive to succeed in globalization.
- The quality of manufactured goods must match international standards to compete globally.
4. Classification of Industries:
I. Based on the Source of Raw Materials:
- Agro-based industries: Cotton, woollen, jute, silk, rubber, sugar, tea, coffee, edible oil.
- Mineral-based industries: Iron and steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools, petrochemicals.
II. Based on Main Role:
- Basic industries: Supply raw materials for other industries (e.g., iron and steel, aluminium smelting).

Source: NCERT Book - Consumer industries: Produce goods for direct consumer use (e.g., sugar, paper, toothpaste).
III. Based on Capital Investment:
- Small-scale industries: Maximum investment in assets is ₹1 crore.
IV. Based on Ownership:
- Public sector: Owned by the government (e.g., BHEL, SAIL).
- Private sector: Owned by individuals or groups (e.g., TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd.).
- Joint sector: Owned jointly by state and private individuals (e.g., Oil India Ltd.).
- Cooperative sector: Owned by producers or workers pooling resources (e.g., sugar industry in Maharashtra, coir industry in Kerala).
V. Based on Bulk and Weight of Raw Materials:
- Heavy industries: Use heavy raw materials (e.g., iron and steel).
- Light industries: Use light raw materials to produce light goods (e.g., electrical goods).
Agricultural-Based Industries
- Examples of agricultural-based industries are cotton, jute, silk, woollen textiles, sugar, and edible oil.
1. Textile Industry:
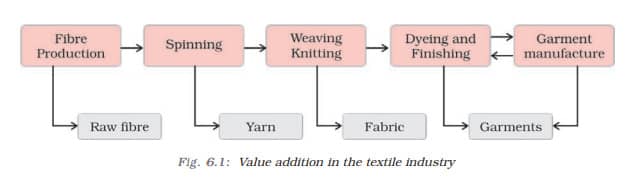
- Contributes significantly to industrial production, employment, and foreign exchange.
- Self-reliant industry: From raw material to finished products.
2. Cotton Textiles:
- Originated with hand spinning and weaving; later replaced by power looms after the 18th century.
- First textile mill: Established in Mumbai in 1854.
- World Wars boosted the cotton textile industry due to British demand.
- Initially concentrated in Maharashtra and Gujarat due to proximity to raw cotton, labour, transport, and market facilities.
- Spinning is centralized, while weaving is decentralized to incorporate traditional designs and skills.
- Handspun khadi provides employment in rural areas.
3. Challenges in Cotton Textiles:
- High-quality yarn is underutilized due to lower-quality weaving.
- Weaving uses handlooms, power looms, and mills.
4. Jute Industry:
- India: Largest producer of raw jute and second in jute exports (after Bangladesh).
- Key factors for location in West Bengal (Hugli Basin):
a. Proximity to raw materials, cheap labour, and water transport.
b. Urban facilities (banking, insurance, export ports). - First jute mill: Rishra, near Kolkata (1855).
5. Sugar Industry:
- India: Second largest sugar producer; first in gur and khandsari.
- The seasonal nature makes it suitable for cooperatives.
- Initially concentrated in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar; now shifting to Maharashtra and southern states for better cane quality and climate.
Mineral-Based Industries
- Definition: Industries using minerals/metals as raw materials.
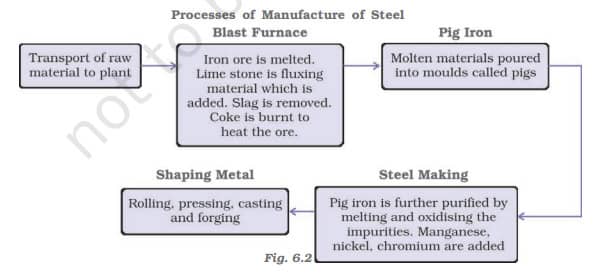
1. Iron and Steel Industry:
- Basic industry: Supports heavy, medium, and light industries.
- Major raw materials: Iron ore, coking coal, limestone (4:2:1 ratio).
- Maximum concentration in Chhotanagpur Plateau due to raw material proximity, cheap labour, and market potential.
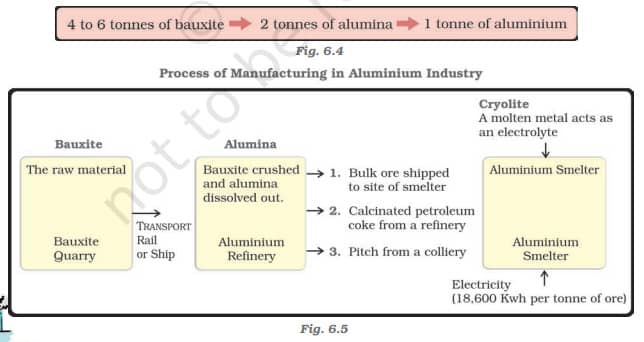
2. Aluminium Smelting:
- Second-most important metallurgical industry.
- Raw material: Bauxite (bulky and reddish rock).
- Factors for location: Electricity supply and raw material availability.
Chemical Industry
- Chemical industries are often located near oil refineries and petrochemical plants.
1. Fast-Growing Sector:
- Includes large and small-scale industries.
2. Inorganic Chemicals:
Examples: Sulfuric acid (fertilizers, dyes), and soda ash (glass, soaps).
3. Organic Chemicals:
- Petrochemicals are used in synthetic fibres, plastics, drugs, etc.
Fertilizer Industry
1. Types of fertilizers:
- Nitrogenous (urea), phosphatic, and complex (NPK).
- Potash is entirely imported due to a lack of reserves.
2. Major production centres:
- Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, and Punjab.
Other Key Industries
1. Cement Industry:
- Raw materials: Limestone, silica, gypsum.
- Essential for construction (buildings, dams, roads, etc.).
2. Automobile Industry:
- Produces vehicles like trucks, buses, cars, and two/three-wheelers.
- Growth post-liberalization due to contemporary models and market demand.
- Major hubs: Delhi, Gurugram, Pune, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bengaluru.
Information Technology and Electronics Industry
Electronics Industry Overview
1. Scope of the Electronics Industry:
- Products include transistor sets, televisions, telephones, cellular telecom, telephone exchanges, radars, computers, and telecommunication equipment.
2. Role in Telecommunication:
- Supports and supplies essential equipment for the telecommunication industry.
Key Locations
1. Electronic Capital of India:
- Bengaluru is recognized as the electronic capital.
2. Other Major Centers:
- Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, and Coimbatore.
3. Industry Concentration:
- Bengaluru, Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, and Pune are key hubs.
Impact on Economy
1. Employment Generation:
- The electronics industry has significantly boosted employment opportunities.
2. IT Industry Success:
- Growth in the hardware and software sectors is pivotal for India’s IT industry’s success.
Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
1. Role of Industries in Pollution:
- Industries contribute to economic growth but also cause significant pollution and environmental degradation.
2. Types of Pollution:
- Industries cause four major types of pollution:
a) Air
b) Water
c) Land
d) Noise
3. Polluting Units:
- Includes industries and thermal power plants.
a. Air Pollution
1. Causes of Air Pollution:
- Undesirable gases like sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Airborne particulate materials: dust, mist, smoke, and sprays.
- Sources:
a. Chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries, and smelting plants.
b. Burning fossil fuels in factories ignoring pollution norms.
2. Impact of Air Pollution:
- Adversely affects human health, animals, plants, buildings, and the atmosphere.
- Toxic gas leaks, e.g., Bhopal Gas Tragedy, can cause long-term hazardous effects.
b. Water Pollution
1. Causes of Water Pollution:
- Organic and inorganic industrial wastes are discharged into rivers.
- Sources:
a. Paper, pulp, chemical, textile, dyeing industries.
b. Petroleum refineries, tanneries, electroplating industries.
c. Substances: dyes, detergents, acids, salts, heavy metals (lead, mercury), fertilizers, pesticides, synthetic d. chemicals, plastics, rubber.
2. Solid Waste Contributors:
- Fly ash, phospho-gypsum, iron and steel slags.
3. Thermal Pollution:
- Hot water discharge from factories and thermal plants into rivers and ponds affects aquatic life.
4. Nuclear Waste Hazards:
- Wastes from nuclear power plants and weapon facilities cause cancers, birth defects, and miscarriages.
c. Land and Soil Pollution
1. Causes of Land Pollution:
- Dumping of industrial waste: glass, harmful chemicals, packaging, salts, garbage.
2. Effect on Soil and Groundwater:
- Pollutants carried by rainwater percolate into the soil and contaminate groundwater.
d. Noise Pollution
1. Causes of Noise Pollution:
- Industrial and construction activities.
- Machinery, factory equipment, generators, saws, pneumatic and electric drills.
2. Effects of Noise Pollution:
- Irritation and anger.
- Hearing impairment, increased heart rate, and blood pressure.
- Noise is a source of stress.
Control of Environmental Degradation
Impact of Industrial Wastewater on Freshwater
1. Wastewater Pollution Ratio:
- Every litre of industrial wastewater pollutes eight times the quantity of freshwater.
Suggestions to Reduce Freshwater Pollution
1. Reuse and Recycling:
Minimise water usage by reusing and recycling in multiple stages.
2. Rainwater Harvesting:
- Utilize harvested rainwater to meet water requirements.
3. Effluent Treatment Before Disposal:
- Treat hot water and effluents before releasing them into water bodies.
- Treatment involves three phases:
a. Primary Treatment: Mechanical methods (screening, grinding, flocculation, sedimentation).
b. Secondary Treatment: Biological Processes.
c. Tertiary Treatment: Combination of biological, chemical, and physical processes (recycling of wastewater).
Regulating Groundwater Use
1. Groundwater Overuse:
- Legal regulation is required to prevent overdrawing of groundwater reserves.
Reducing Air Pollution
1. Particulate Matter Control:
- Install smoke stacks with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers, and inertial separators in factories.
2. Fuel Substitution:
- Use oil or gas instead of coal in factories to reduce smoke emissions.
Minimising Noise Pollution
1. Machinery Modifications:
- Use energy-efficient, noise-reducing machinery and equipment.
- Fit generators with silencers.
2. Noise Absorbing Measures:
- Use noise-absorbing materials and personal protective equipment like earplugs and earphones.
Sustainable Development
1. Integration of Development and Environment:
- Sustainable development requires integrating economic development with environmental protection.
Case Study: NTPC’s Environmental Initiatives
1. ISO Certification:
- NTPC holds ISO 14001 certification for EMS (Environment Management System).
2. Proactive Environmental Preservation:
- Key strategies include:
a. Optimum utilisation of equipment through modern techniques and upgrades.
b. Waste reduction by maximising ash utilisation.
c. Green belt development to maintain ecological balance.
d. Special purpose vehicles for afforestation.
e. Pollution reduction through ash pond management, ash water recycling, and liquid waste management.
f. Ecological monitoring, reviews, and online database management for power stations.
MCQ Questions on NCERT Geography Class 10 Chapter 6 | Importance Of Manufacturing
Question 1. Why is the manufacturing sector considered the backbone of economic development?
A. It modernizes agriculture and provides jobs in the secondary and tertiary sectors
B. It focuses exclusively on agricultural products
C. It aims to reduce exports
D. It discourages industrial development
Answer: A
Question 2. What is the primary goal of public sector industries in India?
A. Increasing imports
B. Establishing industries in tribal and backward areas
C. Reducing industrial output
D. Limiting technological advancements
Answer: B
Question 3. How does exporting manufactured goods benefit the economy?
A. It reduces unemployment
B. It increases self-reliance
C. It brings foreign exchange
D. It limits international trade
Answer: C
Question 4. Which of the following products is NOT provided by agro-industries?
A. Fertilizers
B. Insecticides
C. Aircraft
D. Irrigation pumps
Answer: C
Question 5. What has the development of manufacturing industries done for agriculture?
A. Increased agricultural dependence on imports
B. Made production processes more efficient
C. Replaced traditional agricultural methods
D. Reduced agricultural productivity
Answer: B
Question 6. Which of the following industries is agro-based?
A. Petrochemicals
B. Cement
C. Sugar
D. Machine tools
Answer: C
Question 7. Which industry is categorized as mineral-based?
A. Rubber
B. Cement
C. Cotton textiles
D. Edible oil
Answer: B
Question 8. What defines a small-scale industry in India?
A. Ownership structure
B. Maximum investment in assets
C. Number of employees
D. Type of products manufactured
Answer: B
Question 9. Oil India Ltd. (OIL) is an example of which type of ownership?
A. Public sector
B. Private sector
C. Joint sector
D. Cooperative sector
Answer: C
Question 10. Where was the first successful textile mill in India established?
A. Ahmedabad
B. Mumbai
C. Kolkata
D. Surat
Answer: B
Question 11. Why is the sugar industry ideally suited to the cooperative sector?
A. It is capital-intensive
B. It is seasonal in nature
C. It has a short supply chain
D. It requires minimal labour
Answer: B
Question 12. What raw material is primarily used in the aluminium smelting industry?
A. Iron ore
B. Limestone
C. Bauxite
D. Copper
Answer: C
Question 13. Which state has emerged as the electronic capital of India?
A. Mumbai
B. Bengaluru
C. Hyderabad
D. Chennai
Answer: B
Question 14. What is the primary cause of air pollution by industries?
A. Use of renewable energy sources
B. Presence of sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide
C. Recycling of waste materials
D. High-quality emission standards
Answer: B
Question 15. Which industry contributes significantly to water pollution?
A. Textiles and dyeing
B. Electronics
C. Automobile
D. Cement
Answer: A
Question 16. How can noise pollution in industries be reduced?
A. Increasing fossil fuel usage
B. Installing silencers on equipment
C. Using untreated machinery
D. Ignoring environmental standards
Answer: B
Question 17. Which of the following is NOT a type of industrial pollution?
A. Air pollution
B. Water pollution
C. Light pollution
D. Noise pollution
Answer: C
Question 18. Which of the following is NOT a way to control industrial pollution of freshwater?
A. Reusing and recycling water
B. Discharging untreated effluents
C. Harvesting rainwater
D. Treating hot water before release
Answer: B
Question 19. NTPC has adopted which approach for environmental preservation?
A. Ignoring ash utilization
B. Minimizing waste generation
C. Focusing only on thermal plants
D. Avoiding green belt creation
Answer: B
Question 20. What is a major goal of sustainable development in industries?
A. Maximizing profits at all costs
B. Integrating economic development with environmental concerns
C. Minimizing energy efficiency
D. Promoting unregulated industrial growth
Answer: B
Question 21. Which industry contributes the most to India’s foreign exchange earnings?
A. Chemical industry
B. Textile industry
C. Fertilizer industry
D. Cement industry
Answer: B
Question 22. Which state is a significant producer of fertilizers in India?
A. Gujarat
B. Kerala
C. Tamil Nadu
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Question 23. What type of pollution results from hot water discharge into rivers?
A. Noise pollution
B. Thermal pollution
C. Air pollution
D. Land pollution
Answer: B
Question 24. Which raw material’s sucrose content determines the location of sugar mills?
A. Cotton
B. Jute
C. Cane
D. Rubber
Answer: C
Question 25. The manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of economic development because:
a) It helps modernise agriculture.
b) It reduces dependence on agriculture.
c) It provides jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
d) All of the above.
Answer: d) All of the above
Question 26. Which of the following was a major aim of establishing public sector industries in India?
a) Importing foreign goods.
b) Reducing regional disparities.
c) Increasing agricultural productivity.
d) Encouraging privatisation.
Answer: b) Reducing regional disparities
Question 27. Why is the export of manufactured goods significant?
a) It increases agricultural output.
b) It brings in foreign exchange.
c) It creates unemployment.
d) It decreases trade and commerce.
Answer: b) It brings in foreign exchange
Question 28. How do agro-industries assist agriculture?
a) By boosting productivity.
b) By providing irrigation pumps and fertilisers.
c) By increasing efficiency in production processes.
d) All of the above.
Answer: d) All of the above
Question 29. What is necessary for India to compete in the global market?
a) High-quality manufactured goods.
b) Focus on self-sufficiency only.
c) Dependency on agricultural exports.
d) Production of low-cost goods only.
Answer: a) High-quality manufactured goods
Question 30. An example of an agro-based industry is:
a) Cement.
b) Aluminium smelting.
c) Jute.
d) Petrochemicals.
Answer: c) Jute
Question 31. Which industry supplies raw materials to manufacture other goods?
a) Consumer industry.
b) Basic or key industry.
c) Light industry.
d) Heavy industry.
Answer: b) Basic or key industry
Question 32. What is the maximum investment allowed in small-scale industries?
a) ₹10 lakh.
b) ₹50 lakh.
c) ₹1 crore.
d) ₹5 crore.
Answer: c) ₹1 crore
Question 33. Cooperative sector industries are:
a) Owned by individuals.
b) Owned and operated by government agencies.
c) Owned and operated by producers or workers.
d) Jointly run by public and private sectors.
Answer: c) Owned and operated by producers or workers
Question 34. Light industries produce:
a) Heavy goods.
b) Light goods like electrical appliances.
c) Machinery and tools.
d) Vehicles.
Answer: b) Light goods like electrical appliances
Question 35. The first textile mill in India was established in:
a) Chennai.
b) Kolkata.
c) Mumbai.
d) Delhi.
Answer: c) Mumbai
Question 36. India ranks second in the production of:
a) Cotton textiles.
b) Jute goods.
c) Sugar.
d) Cement.
Answer: b) Jute goods
Question 37. The handspun khadi provides:
a) Low-quality fabric.
b) Mass employment in rural areas.
c) Competition to mill-made cloth.
d) No economic benefit.
Answer: b) Mass employment in rural areas
Question 38. Which is considered a basic industry?
a) Fertiliser.
b) Textile.
c) Iron and steel.
d) Automobile.
Answer: c) Iron and steel
Question 39. Aluminium is widely used because:
a) It is heavy.
b) It is resistant to corrosion.
c) It is an expensive metal.
d) It has low conductivity.
Answer: b) It is resistant to corrosion
Question 40. Air pollution is caused by:
a) Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
b) Increased nitrogen levels.
c) Groundwater depletion.
d) Low soil fertility.
Answer: a) Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide
Question 41. What is the primary cause of thermal water pollution?
a) Discharge of untreated chemicals.
b) Release of untreated hot water into rivers.
c) Excessive water usage in industries.
d) Leakage of nuclear waste.
Answer: b) Release of untreated hot water into rivers
Question 42. Which measure can reduce industrial water pollution?
a) Harvesting rainwater.
b) Recycling effluents.
c) Treating waste before disposal.
d) All of the above.
Answer: d) All of the above
Question 43. The electronics industry is mainly concentrated in:
a) Chennai, Bengaluru, Pune, and Mumbai.
b) Delhi, Kolkata, Lucknow, and Jamshedpur.
c) Hyderabad, Indore, and Bhubaneswar.
d) Patna, Ranchi, and Dehradun.
Answer: a) Chennai, Bengaluru, Pune, and Mumbai
Question 44. NTPC has adopted which approach for environmental preservation?
a) Maximising waste production.
b) Using outdated techniques.
c) Minimising ash utilisation.
d) Creating green belts for ecological balance.
Answer: d) Creating green belts for ecological balance
Question 45. The fertiliser industry in India produces:
a) Only nitrogenous fertilisers.
b) Phosphatic fertilisers, nitrogen, and potash.
c) Nitrogenous and phosphatic fertilisers but imports potash.
d) None of the above.
Answer: c) Nitrogenous and phosphatic fertilisers but imports potash
Question 46. What is the primary raw material for the cement industry?
a) Coal.
b) Gypsum.
c) Bauxite.
d) Limestone.
Answer: d) Limestone