NCERT Geography Class 10 | Land Use Pattern In India
Topic & sub-topics covered: Land Use Pattern In India: Resources and Development (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 10th about “Land Use Pattern In India” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 10th chapter 1st “Resources and Development“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 10th Chapter 1 Resources and Development PDF
NCERT Geography for Class 10th Chapter 1 Resources and Development PDF offers students a comprehensive guide to understanding resources, their types, and sustainable management. NCERT Geography for Class 10th Chapter 1: Resources and Development delves into natural, human, and human-made resources, emphasizing the need for careful utilization and conservation.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 10th Chapter 1 Resources and Development PDF
It covers resource planning, conservation techniques, and the impact of technology on resource management. This PDF aligns with the CBSE curriculum, providing well-structured content for easy study and revision. The chapter emphasizes the balance between current resource use and preserving future needs, focusing on sustainable development principles.
Land Use Pattern In India
1. Factors Influencing Land Use:
- Physical Factors: Land use is influenced by topography, climate, and soil types.
- Human Factors: Population density, technological capability, culture, and traditions also determine land use patterns.
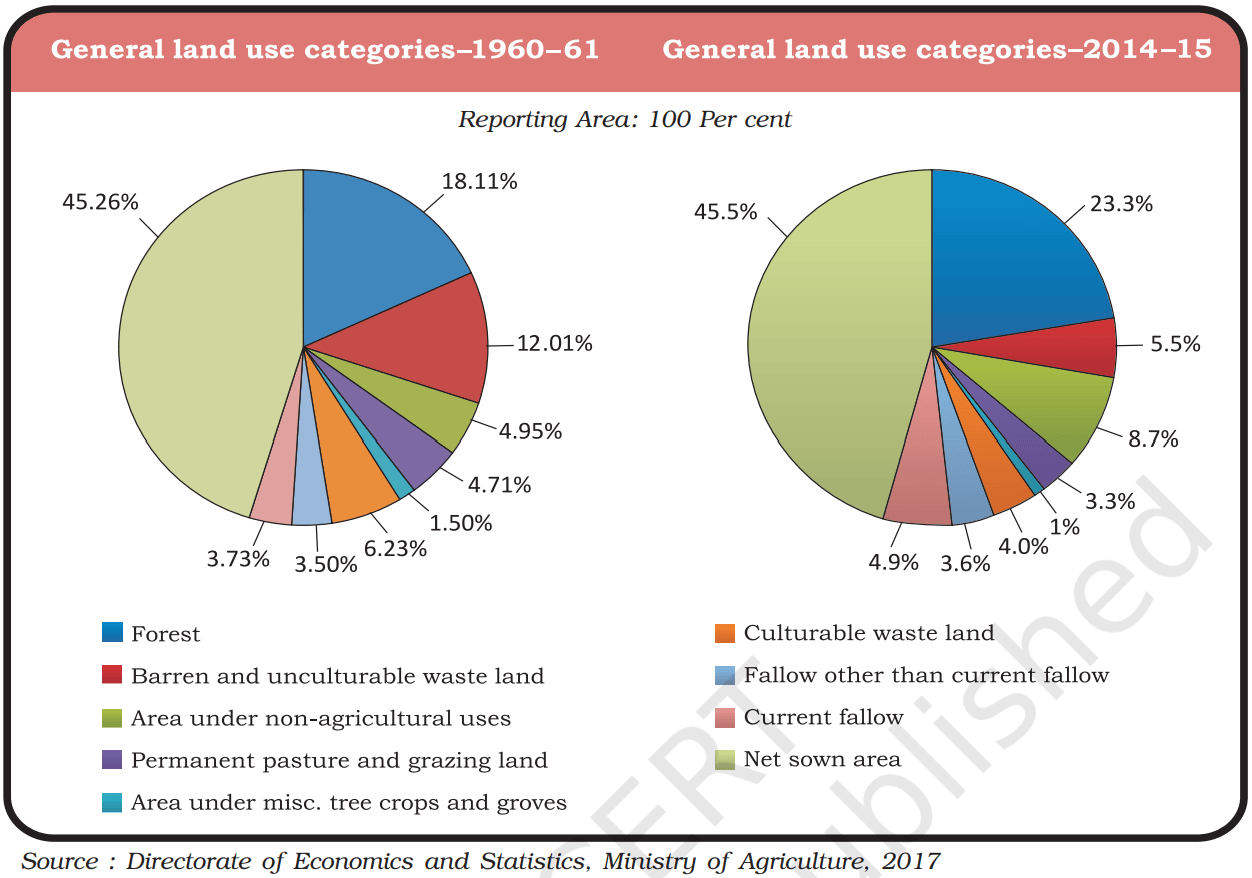
2. Land Use Data in India:
- India’s total geographical area is 3.28 million sq. km.
- Land use data is available for 93% of this area; the remaining 7% includes parts of the northeast (except Assam) and areas in Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China, which have not been fully surveyed.
3. Issues with Land Use:
- Decrease in Permanent Pasture: The reduction in pasture land raises concerns about feeding India’s large cattle population.
- Quality of Non-Fallow Lands: Many non-fallow lands are of poor quality or have high cultivation costs, leading to infrequent cultivation.
4. Net Sown Area (NSA):
- If poor-quality lands are included, the NSA in India accounts for about 54% of the total reporting area.
- State Variations in NSA:
a. Over 80% of the total area in Punjab and Haryana is net sown.
b. Less than 10% of the total area is net sown in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur, and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
5. Forest Area in India:
- The forest area is significantly below the National Forest Policy’s target of 33% of the geographical area.
- Adequate forest cover is essential for maintaining ecological balance and supporting the livelihoods of millions living on forest fringes.
6. Waste Land and Non-Agricultural Uses:
- Waste Land: Includes rocky, arid, and desert areas.
- Land for Non-Agricultural Uses: Includes land for settlements, roads, railways, and industries.
7. Land Degradation:
- Continuous land use without proper conservation and management leads to land degradation.
- Land degradation has serious social and environmental consequences.