Accountable, Responsive And Legitimate Government – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic & sub-topics covered: “Accountable, Responsive And Legitimate Government” and MCQs Questions: Outcomes of Democracy (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 10th about “Accountable, Responsive And Legitimate Government” from the NCERT Political Science (Civics) notes for class 10th chapter 5 “Outcomes of Democracy“.
Download the NCERT Political Science (Civics) for Class 10 Chapter 5 Outcomes of Democracy PDF Notes
Download the NCERT Political Science (Civics) Class 10 Chapter 5 “Outcomes of Democracy” PDF Notes to revise key concepts quickly. This chapter explains how democracy affects a country’s governance, economy, social equality, and citizen rights. It discusses whether democratic systems meet people’s expectations by being accountable, inclusive, and respecting individual dignity. These notes offer a clear, concise summary—perfect for exam prep or quick understanding.
Accountable, Responsive And Legitimate Government

1. Basic Outcomes of Democracy:
- Democracy ensures the right of citizens to choose their rulers.
- It provides control over rulers through participation in decision-making when necessary.
- A key outcome of democracy is the establishment of a government that is:
a. Accountable to citizens.
b. Responsive to the needs and expectations of the people.
2. Efficiency and Effectiveness of Democratic Governments:
- Criticism: Democracy is often seen as less efficient due to delays in decision-making.
- Comparison with Non-Democracy:
a. Non-democratic governments are quicker as they don’t need deliberation or majority support.
b. However, such decisions may lack acceptance and face resistance. Democratic Decision-Making:
a. Slower but follows procedures.
b. Leads to decisions that are more acceptable and effective.
3. Transparency in Democracy:
- Democracy ensures decision-making is based on norms and procedures.
- Citizens can verify if decisions were made correctly, ensuring transparency.
- Transparency is often absent in non-democratic governments.
4. Mechanisms of Accountability in Democracy:
- Democracies develop mechanisms to:
a. Hold the government accountable.
b. Enable citizen participation in decision-making.
5. Practices and Institutions of Democracy:
- Features that measure democratic outcomes:
a. Regular, free, and fair elections.
b. Open public debates on policies and legislation.
c. Right to information about government functioning. - Mixed Record:
a. Democracies excel in regular elections and debates.
b. Democracies often fail to ensure fairness in elections and full transparency in decisions.
6. Substantive Expectations from Democracy:
- Citizens expect:
a. A government attentive to people’s needs and demands.
b. A system largely free of corruption. - Reality:
a. Democracies often fail to meet these expectations.
b. Corruption and neglect of the majority’s demands are common.
7. Comparison of Democracy and Non-Democracy:
- Democracies vs. Non-Democracies:
a. Democracies are not completely free of corruption or insensitivity.
b. Non-democracies show no evidence of being less corrupt or more responsive.
8. Legitimacy of Democratic Governments:
- Democracies are legitimate governments because:
a. They are elected by the people.
b. They generate support through representation. - Despite being slow, less efficient, and not always responsive, democracy is widely supported worldwide.
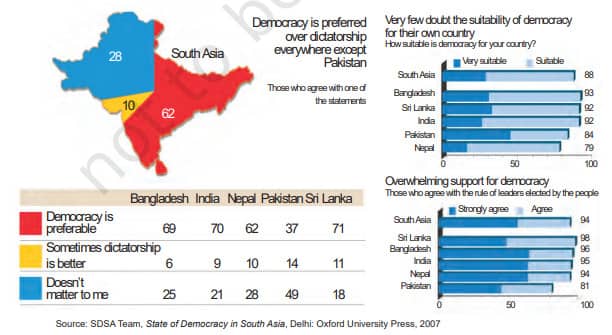
9. Public Perception of Democracy:
- People believe:
a. Democracy is suitable for their country.
b. Representatives elected by them should rule. - Democracy generates its support, an outcome that cannot be ignored.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Political Science (Civics) Class 10 Chapter 5: Outcomes of Democracy
MCQs on NCERT Civics Class 10 Chapter 5 Topic – Accountable, Responsive And Legitimate Government
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Accountable, Responsive And Legitimate Government” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. What is the most basic outcome of democracy?
(a) Quick decision-making
(b) Accountability and responsiveness to citizens
(c) Centralised power
(d) Economic growth
Answer: (b) Accountability and responsiveness to citizens
Question 2. Why do democratic governments take longer to make decisions?
(a) Because they are inefficient
(b) Because they follow norms and procedures
(c) Because they rely on non-democratic institutions
(d) Because they avoid public opinion
Answer: (b) Because they follow norms and procedures
Question 3. What is a key feature of democracy that allows citizens to check the decision-making process?
(a) Speed in decision-making
(b) Military enforcement
(c) Transparency
(d) Arbitrary governance
Answer: (c) Transparency
Question 4. What does transparency in a democratic government ensure?
(a) Citizens can verify if decisions followed the correct procedures
(b) Decisions are made without public input
(c) Non-democratic norms are upheld
(d) Elections are avoided
Answer: (a) Citizens can verify if decisions followed the correct procedures
Question 5. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a democratic government?
(a) Regular, free, and fair elections
(b) Open public debate on policies
(c) Centralised decision-making
(d) Citizens’ right to information
Answer: (c) Centralised decision-making
Question 6. What is a common criticism of democracy regarding elections?
(a) Elections are never conducted
(b) They do not always provide a fair chance to everyone
(c) Elections do not involve the public
(d) Elections happen only in non-democratic regimes
Answer: (b) They do not always provide a fair chance to everyone
Question 7. What is the expected outcome of democracy in terms of governance?
(a) Complete elimination of corruption
(b) A government that is attentive to the people’s needs
(c) Rapid policy implementation without debate
(d) A fixed economic growth rate
Answer: (b) A government that is attentive to the people’s needs
Question 8. Why is democracy considered better than non-democracy despite corruption?
(a) It is the people’s government
(b) It eliminates corruption entirely
(c) It avoids public participation
(d) It imposes strict laws without accountability
Answer: (a) It is the people’s government
Question 9. What outcome of democracy is highlighted by its legitimacy?
(a) It creates a sense of ownership among citizens
(b) It is less sensitive to public needs
(c) It relies on military power for governance
(d) It guarantees economic equality
Answer: (a) It creates a sense of ownership among citizens
Question 10. Which aspect of democracy generates its own support among citizens?
(a) Economic growth
(b) Rule by religious leaders
(c) Elections and representation
(d) Authoritarian control
Answer: (c) Elections and representation

