Wildlife – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: Wildlife and MCQs Questions: Natural Vegetation And Wildlife (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “Wildlife” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 9th chapter 5 “Natural Vegetation And Wildlife“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Notes PDF
Let’s be honest, remembering the details of Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife can feel overwhelming with all the forest types, seasonal changes, and animal species. That’s why I’ve put together these notes in a clear and simple format. You’ll find everything explained step by step – like how monsoon patterns shape vegetation or why certain wildlife is unique to specific regions. These notes aren’t just summaries, they’re designed to help you connect the concepts with real examples. You can also download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Notes PDF for quick revision anytime.
Wildlife
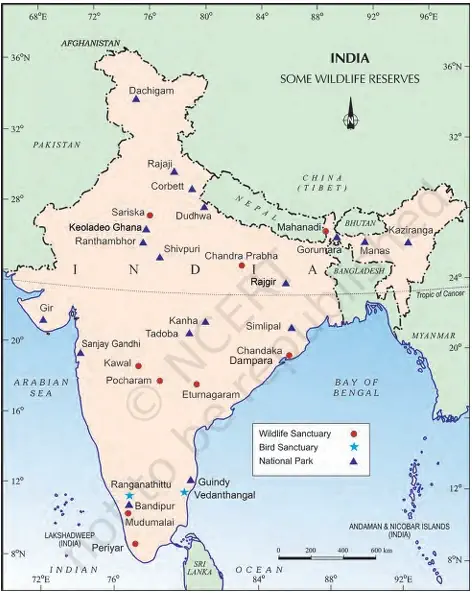
1. India’s Faunal Richness:
- India has about 90,000 animal species.
- About 2,000 species of birds, i.e., 13% of the world’s total.
- About 2,546 species of fish, i.e., 12% of the world’s stock.
- India shares 5–8% of the world’s amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
2. Major Animals in Different Regions:
- Elephants – found in hot wet forests of Assam, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- One-horned rhinoceroses – in swampy & marshy lands of Assam and West Bengal.
- Wild ass – Rann of Kachchh.
- Camels – Thar Desert.
- Other animals – Indian bison, nilgai (blue bull), chousingha (four-horned antelope), gazelle, and deer species.
- Several species of monkeys are also found.
3. Big Cats in India:
- India is the only country in the world with both lions and tigers.
- Indian lion – natural habitat: Gir Forest, Gujarat.
- Tigers – found in Madhya Pradesh, Sundarbans (West Bengal), and Himalayan region.
- Leopards – important animals of prey.
4. Himalayan & Ladakh Wildlife:
- Himalayas – harbour hardy animals surviving extreme cold.
- Ladakh’s high altitudes – yak (wild ox, ~1 tonne), Tibetan antelope, bharal (blue sheep), wild sheep, kiang (Tibetan wild ass).
- Other species – ibex, bear, snow-leopard, red panda.
5. Aquatic & Bird Life:
- Rivers, lakes & coastal areas – turtles, crocodiles, gharials.
- Gharial – only representative of a crocodile variety worldwide.
- Common birds – peacocks, pheasants, ducks, parakeets, cranes, pigeons.

6. Role of Biodiversity:
- Crops selected from a bio-diverse environment.
- Many medicinal plants also identified.
- Animals used as milch animals, draught power, transport, meat, and eggs.
- Fish provide nutritive food.
- Insects help in pollination and biological control of harmful insects.
- Every species has a role in the ecosystem – hence conservation is essential.
7. Threats to Flora & Fauna:
- About 1,300 plant species endangered; 20 species extinct.
- Many animal species are endangered; some already extinct.
- Causes of threat:
a. Hunting by greedy hunters.
b. Pollution from chemicals & industrial waste.
c. Acid deposits.
d. Alien species introduction.
e. Reckless deforestation for cultivation & habitation.
8. Government Conservation Measures:
- 18 Biosphere Reserves set up in India.
- 12 reserves included in the world network of biosphere reserves:
- Sundarbans, Nanda Devi, Gulf of Mannar, Nilgiri, Nokrek, Great Nicobar, Simlipal, Pachmarhi, Achanakmar-Amarkantak, Agasthyamalai, Kangchendzonga, Panna.
- Since 1992, financial & technical help given to botanical gardens.
- Eco-projects: Project Tiger, Project Rhino, Project Great Indian Bustard.
- Protected Areas: 106 National Parks, 573 Wildlife Sanctuaries, several Zoological gardens.
9. Fact File:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 implemented in India.
- Message – Natural ecosystem is vital for survival; destruction must stop immediately.
Eighteen Bio-reserves
- Sundarbans
- Simlipal
- Gulf of Mannar
- Dihang-Dibang
- Nilgiri
- Nanda Devi
- Nokrek
- Great Nicobar
- Manas
- Kachchh
- Dibru Saikhowa
- Agasthyamalai
- Kangchendzonga
- Pachmarhi
- Achanakmar-Amarkantak
- Cold Desert
- Seshachalam
- Panna
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Geography Class 9 Chapter 5: Natural Vegetation And Wildlife
| Topics No. | Topics Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Types Of Vegetation |
| 2 | Wildlife |
MCQs on NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 5 Topic – Wildlife
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Wildlife” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. Approximately how many animal species are found in India?
a) 80,000
b) 85,000
c) 90,000
d) 1,00,000
Answer: c) 90,000
Question 2. How many species of birds are found in India?
a) 1,500
b) 2,000
c) 2,546
d) 6,000
Answer: b) 2,000
Question 3. India’s birds constitute about what percentage of the world’s total?
a) 10%
b) 11%
c) 12%
d) 13%
Answer: d) 13%
Question 4. How many species of fish are found in India?
a) 1,500
b) 2,000
c) 2,546
d) 3,000
Answer: c) 2,546
Question 5. Indian fish species account for nearly what percent of the world’s stock?
a) 8%
b) 10%
c) 12%
d) 15%
Answer: c) 12%
Question 6. India shares what percentage of the world’s amphibians, reptiles and mammals?
a) 3–5%
b) 4–6%
c) 5–8%
d) 8–10%
Answer: c) 5–8%
Question 7. The most majestic animals among the mammals of India are:
a) Lions
b) Elephants
c) Tigers
d) Rhinos
Answer: b) Elephants
Question 8. Elephants are found in the hot wet forests of:
a) Rajasthan and Gujarat
b) Assam, Karnataka and Kerala
c) Madhya Pradesh and Punjab
d) West Bengal and Orissa
Answer: b) Assam, Karnataka and Kerala
Question 9. One-horned rhinoceroses live in:
a) Rajasthan and Gujarat
b) Assam and West Bengal
c) Tamil Nadu and Kerala
d) Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh
Answer: b) Assam and West Bengal
Question 10. Which animals are found in arid areas of Rann of Kachchh and Thar Desert respectively?
a) Camel and Wild Ass
b) Wild Ass and Camel
c) Deer and Tiger
d) Gazelle and Leopard
Answer: b) Wild Ass and Camel
Question 11. The natural habitat of the Indian lion is:
a) Sundarbans
b) Gir forest, Gujarat
c) Himalayas
d) Nilgiris
Answer: b) Gir forest, Gujarat
Question 12. Tigers in India are found in:
a) Madhya Pradesh, Sundarbans, Himalayas
b) Assam, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh
c) Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana
d) Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu
Answer: a) Madhya Pradesh, Sundarbans, Himalayas
Question 13. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
a) Yak – Ladakh
b) Tibetan antelope – Cold deserts
c) Royal Bengal Tiger – Sundarbans
d) Elephant – Rajasthan desert
Answer: d) Elephant – Rajasthan desert
Question 14. The only representative of a crocodile variety found in the world today is:
a) Turtle
b) Gharial
c) Crocodile
d) Monitor lizard
Answer: b) Gharial
Question 15. Which of these animals is NOT found in Ladakh?
a) Yak
b) Kiang (Tibetan wild ass)
c) Snow leopard
d) Lion
Answer: d) Lion
Question 16. The rare red panda is found in:
a) Gujarat
b) Ladakh pockets
c) Nilgiris
d) Andaman Islands
Answer: b) Ladakh pockets
Question 17. Which bird is the national bird of India?
a) Parrot
b) Peacock
c) Crane
d) Pigeon
Answer: b) Peacock
Question 18. Which of the following birds are common in Indian forests and wetlands?
a) Peacocks, ducks, parakeets, cranes
b) Penguins, owls, swans
c) Ostrich, pelican, hummingbird
d) Emu, eagle, macaw
Answer: a) Peacocks, ducks, parakeets, cranes
Question 19. Which of the following is a contribution of insects to human life?
a) Providing meat and eggs
b) Providing draught power
c) Helping in pollination and biological control
d) Providing timber
Answer: c) Helping in pollination and biological control
Question 20. Which of the following animals are milch animals (providing milk)?
a) Fish
b) Goats and cows
c) Crocodiles
d) Turtles
Answer: b) Goats and cows
Question 21. About how many plant species are endangered in India?
a) 900
b) 1,300
c) 2,000
d) 5,000
Answer: b) 1,300
Question 22. How many plant species are already extinct in India?
a) 10
b) 15
c) 20
d) 25
Answer: c) 20
Question 23. Which of the following is not a cause of threat to wildlife?
a) Hunting
b) Industrial waste pollution
c) Cutting forests
d) Biological control of harmful insects
Answer: d) Biological control of harmful insects
Question 24. How many biosphere reserves have been set up in India?
a) 12
b) 15
c) 18
d) 20
Answer: c) 18
Question 25. How many of India’s biosphere reserves are included in the World Network?
a) 10
b) 11
c) 12
d) 15
Answer: c) 12
Question 26. Which of the following is not included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves?
a) Sundarbans
b) Nanda Devi
c) Gir Forest
d) Great Nicobar
Answer: c) Gir Forest
Question 27. Project Tiger, Project Rhino and Project Great Indian Bustard are:
a) Agricultural schemes
b) Educational projects
c) Eco-developmental projects
d) Irrigation schemes
Answer: c) Eco-developmental projects
Question 28. How many National Parks are there in India?
a) 73
b) 90
c) 106
d) 120
Answer: c) 106
Question 29. How many wildlife sanctuaries are there in India?
a) 373
b) 473
c) 573
d) 600
Answer: c) 573
Question 30. In which year was the Wildlife Protection Act implemented in India?
a) 1952
b) 1962
c) 1972
d) 1982
Answer: c) 1972

