Topic & sub-topics covered: Formal Sector Credit in India, Formal and Informal Credit: Who gets what?: Money and Credit (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 10th about “Formal Sector Credit in India, Formal and Informal Credit: Who gets what?” which is taken from the NCERT Economics notes for class 10th chapter 3 “Money and Credit“.
Download the NCERT Economics for Class 10th Chapter 3 Money and Credit Notes PDF
Looking to grasp the concepts of money and credit in NCERT Economics for Class 10th? Look no further! Download the comprehensive Chapter 3 Money and Credit Notes PDF now and unlock a treasure trove of knowledge.
NCERT Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit Class 10th PDF Notes
Delve into the intricacies of monetary systems, explore the role of credit in the economy, and understand the mechanisms of banking and financial institutions. Our meticulously prepared notes provide concise explanations, illustrative examples, and insightful analysis to deepen your understanding of this crucial subject. With a clear focus on exam preparation and academic excellence, our PDF notes offer a structured approach to learning, helping you grasp complex concepts with ease.
Gain confidence in your knowledge and ace your exams with the help of our top-quality study material. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to elevate your learning experience – download the NCERT Economics for Class 10th Chapter 3 Money and Credit Notes PDF today!
Formal Sector Credit in India
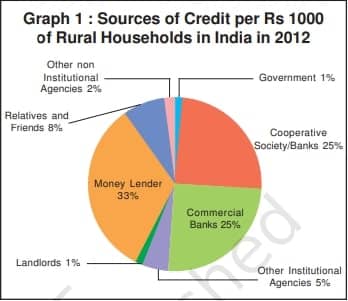
1. Formal Sector vs. Informal Sector Loans:
- Loans obtained from banks and cooperatives constitute formal sector loans.
- Informal sector loans include those obtained from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, and friends.
2. Supervision by Reserve Bank of India (RBI):
- RBI oversees the functioning of formal lenders like banks to ensure compliance with regulations.
- It monitors factors such as maintaining minimum cash balances, diversification of lending, and submission of lending data.
3. Absence of Supervision in the Informal Sector:
- Informal lenders operate without oversight, allowing them to set interest rates and employ unfair practices without regulation.
4. Cost of Borrowing:
- Informal lenders typically charge higher interest rates compared to formal lenders, resulting in a higher cost of borrowing for borrowers.
- This high cost reduces the disposable income of borrowers, impacting their financial stability.
5. Risk of Debt Trap:
- The high-interest rates in the informal sector can lead to increasing debt burdens for borrowers, potentially trapping them in debt cycles.
- Borrowers may struggle to repay loans, risking financial ruin and hindering their ability to start businesses or invest in ventures.
6. Importance of Affordable Credit:
- Affordable credit from formal lenders like banks and cooperatives is essential for economic development.
- Access to cheap credit enables individuals to invest in agriculture, businesses, and small-scale industries, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
Formal and Informal Credit: Who gets what?
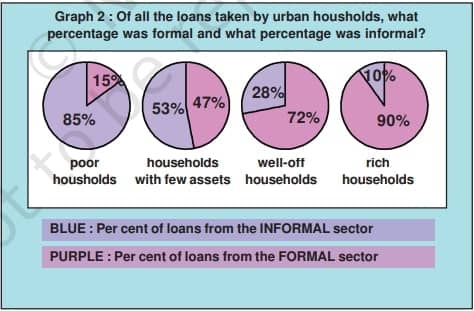
1. Urban Credit Scenario:
- Graph 2 illustrates the distribution of credit sources among urban households, categorized based on economic status.
- Poor urban households rely significantly on informal sources, with 85% of their loans sourced informally.
- In contrast, only 10% of loans taken by rich urban households are from informal sources, with 90% sourced formally.
2. Rural Credit Patterns:
- Similar trends are observed in rural areas, where rich households predominantly access formal credit, while poor households resort to informal sources.
- The disparity highlights the unequal access to affordable credit between different economic groups.
3. Credit Needs in Rural Areas:
- Despite the importance of formal credit, it only fulfils around half of the total credit requirements in rural regions.
- A significant portion of rural credit needs is still met through informal sources due to various factors.
4. High-Interest Rates of Informal Loans:
- Loans from informal lenders typically carry exorbitant interest rates, imposing financial burdens on borrowers.
- These loans often fail to contribute substantially to the income generation of borrowers.
5. Role of Formal Sector Expansion:
- There’s a pressing need for banks and cooperatives to increase lending in rural areas to reduce dependence on informal credit sources.
- Expanding formal sector lending can alleviate the financial strain on borrowers and stimulate economic growth in rural communities.
6. Equitable Distribution of Formal Credit:
- Efforts should be made to ensure that formal credit is distributed more equitably across all economic strata.
- Equal access to formal credit can empower impoverished households by providing them with cheaper loan options, thereby fostering financial inclusion and socio-economic development.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Economics Class 10 Chapter 3: Money and Credit
FAQ
Q1. What distinguishes formal sector loans from informal sector loans?
Answer: Formal sector loans come from banks and cooperatives, while informal sector loans include those from moneylenders, traders, and acquaintances.
Q2. How does borrowing from informal lenders impact borrowers?
Answer: High-interest rates in the informal sector can trap borrowers in debt cycles, hindering financial stability and economic opportunities.
Q3. What patterns are observed in rural credit distribution?
Answer: Similar trends exist in rural areas, with rich households relying on formal credit and poor households resorting to informal sources.
Q4. What challenges are associated with informal loans?
Answer: Informal loans carry high-interest rates and often fail to contribute significantly to borrowers’ income generation.

