Global Poverty Scenario – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: Global Poverty Scenario and MCQs Questions: Poverty as a Challenge (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “Global Poverty Scenario“ from the NCERT Economics notes for class 9th chapter 3 Poverty as a Challenge.
Download the NCERT Economics for Class 9th Chapter 3 Poverty as a Challenge Notes PDF
Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge in Class 9 Economics deals with one of the most pressing social issues in India. The chapter explains how poverty is measured, its causes, and the everyday struggles faced by poor households. Many students often find the terms like “social exclusion” or “vulnerability” tricky, so these notes break them down with examples that are easy to follow. You’ll also get a clear picture of government schemes and policies aimed at reducing poverty. Download the NCERT Economics for Class 9th Chapter 3 Poverty as a Challenge Notes PDF to revise key points quickly and confidently.
Global Poverty Scenario
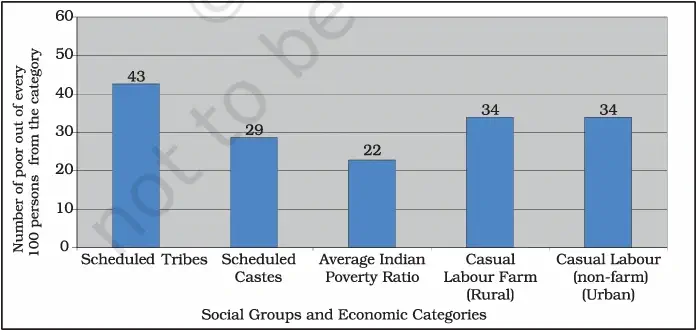
1. International Standard for Poverty Line:
- Global poverty comparisons use a uniform standard set by World Bank.
- Standard = $2.15 per person per day (extreme poverty line).
- Reason for dollar: every country has its own currency, so US dollar is used for uniform comparison.
2. Global Decline in Poverty:
- Extreme poverty declined globally from 16.27% (2010) to 9.05% (2019).
- Shows substantial global reduction but with regional differences.
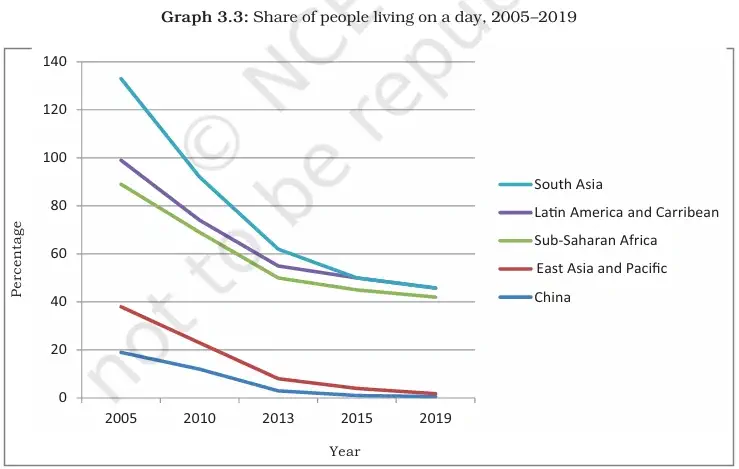
3. China and Southeast Asia:
- Major decline due to rapid economic growth + investment in human resource development.
- In China, poverty fell drastically to 0.1% in 2020.
4. South Asia (India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Afghanistan, Maldives):
- Poverty decline was rapid.
- 2017 – 13%
- 2021 – 11%
- Number of poor reduced from 233 million (2017) to 207 million (2021).
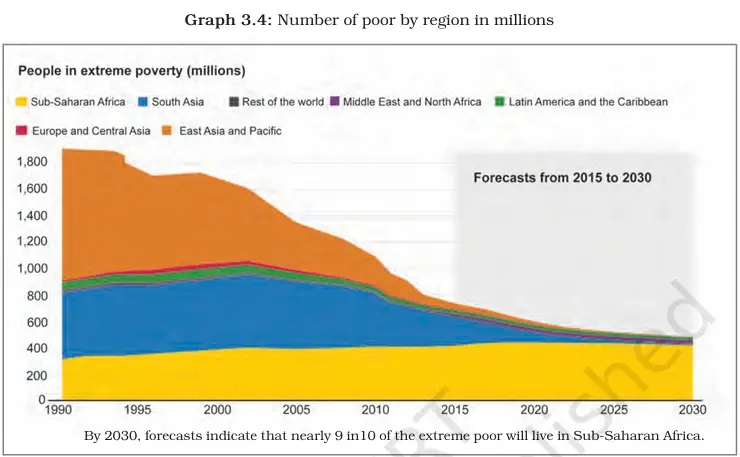
5. Sub-Saharan Africa:
- Poverty declined slightly.
- 2017 – 36.6%
- 2019 – 35%
6. Latin America & Caribbean:
- Poverty ratio increased.
- 2017 – 4.4%
- 2021 – 4.6%
7. Former Socialist Countries:
- Poverty resurfaced at 3% in 2000.
- Example: Russia, where earlier it was officially non-existent.
8. Exam Tip:
- Lowest poverty: China (0.1% in 2020).
- Highest poverty: Sub-Saharan Africa (around 35%).
- South Asia: steady decline, but still significant numbers.
- Latin America & Caribbean: slight increase.
- Russia & former socialist countries: poverty reappeared (3%).
Poverty and Sustainable Development Goals
1. UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Adopted by the United Nations (UN) to provide a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity.
- 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were introduced.
- Aim: Balance people, planet, and prosperity.
2. Ending Poverty:
- Target year: 2030 – End poverty of all types, in all forms, everywhere.
- Requires urgent action by both developed and developing countries.
3. Role of Developed Countries:
- Expected to support developing countries in:
a. Ending poverty
b. Improving health and education
c. Reducing inequalities
d. Tackling climate change
e. Promoting sustainable development
4. UN and Member Countries:
- UN works in collaboration with member governments.
- Each goal is broken into specific targets for countries to achieve.
5. Example: SDG 1 – No Poverty:
- Target: Reduce by half the proportion of men, women, and children of all ages living in poverty (all dimensions) by 2030.
- India’s decline in poverty shows its commitment to Goal 1 (No Poverty).
6. Exam Tip:
- Total SDGs = 17.
- Target year = 2030.
- Goal 1 = No Poverty.
- Key focus = ending poverty in all forms, reducing inequality, sustainable growth, tackling climate change.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Economics Class 9 Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge
MCQs on NCERT Economics Class 9 Chapter 3 Topic – Global Poverty Scenario
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Global Poverty Scenario” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. Which international organisation uses a uniform standard for measuring poverty across countries?
a) International Monetary Fund
b) World Bank
c) United Nations
d) World Trade Organization
Answer: b) World Bank
Question 2. The World Bank defines extreme economic poverty as living on less than:
a) $1.25 per person per day
b) $2.15 per person per day
c) $3.50 per person per day
d) $5 per person per day
Answer: b) $2.15 per person per day
Question 3. The proportion of people in the world living below $2.15 per day declined from 16.27% in 2010 to ____ in 2019.
a) 11.3%
b) 9.05%
c) 8.7%
d) 12.2%
Answer: b) 9.05%
Question 4. Why is the dollar ($) used in international poverty comparisons?
a) Because all countries use the dollar
b) Because the US is the richest country
c) Because the dollar allows comparison across countries with different currencies
d) Because rupee is weaker
Answer: c) Because the dollar allows comparison across countries with different currencies
Question 5. Which country reduced its poverty to just 0.1% in 2020 due to rapid growth and human resource investments?
a) India
b) China
c) Nepal
d) Sri Lanka
Answer: b) China
Question 6. In South Asia, poverty declined from 13% in 2017 to ____ in 2021.
a) 15%
b) 9%
c) 11%
d) 7%
Answer: c) 11%
Question 7. The number of poor in South Asia declined from 233 million in 2017 to ____ in 2021.
a) 220 million
b) 207 million
c) 190 million
d) 150 million
Answer: b) 207 million
Question 8. Which region had poverty decline only slightly from 36.6% in 2017 to 35% in 2019?
a) Latin America
b) Sub-Saharan Africa
c) South Asia
d) Southeast Asia
Answer: b) Sub-Saharan Africa
Question 9. In Latin America and the Caribbean, poverty ratio:
a) Declined to 3% in 2021
b) Increased from 4.4% in 2017 to 4.6% in 2021
c) Remained constant at 4.4%
d) Fell sharply to below 2%
Answer: b) Increased from 4.4% in 2017 to 4.6% in 2021
Question 10. Poverty resurfaced in Russia and some former socialist countries at about:
a) 5% in 2010
b) 3% in 2000
c) 4.4% in 2017
d) 2% in 2019
Answer: b) 3% in 2000
Question 11. The UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) propose to end poverty of all types by:
a) 2025
b) 2030
c) 2040
d) 2050
Answer: b) 2030
Question 12. How many Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were adopted by the UN?
a) 10
b) 15
c) 17
d) 20
Answer: c) 17
Question 13. Which SDG goal directly focuses on ending poverty in all its forms everywhere?
a) Goal 1
b) Goal 5
c) Goal 10
d) Goal 17
Answer: a) Goal 1
Question 14. One of the targets of SDG 1 is to reduce the proportion of people living in poverty by at least:
a) One-third
b) Half
c) Two-thirds
d) One-fourth
Answer: b) Half
Question 15. The success of SDGs requires:
a) Action only by developing countries
b) Action only by developed countries
c) Joint urgent action by both developed and developing countries
d) Only financial support from World Bank
Answer: c) Joint urgent action by both developed and developing countries
Question 16. The UN’s SDGs provide a shared blueprint for:
a) Global trade
b) Peace and prosperity for people and the planet
c) Expanding military power
d) Technology and digitalisation only
Answer: b) Peace and prosperity for people and the planet

