Population Size And Distribution – Concept & Notes PDF
Topic covered: Population Size And Distribution and MCQs Questions: Population (All single detail notes are exam-oriented).
We have discussed in-depth and exam-oriented pointers that can be asked in the board exam of class 9th about the “Population Size And Distribution” from the NCERT Geography notes for class 9th chapter 6 “Population“.
Download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 6 Population Notes PDF
NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 6 – Population Notes & MCQ’s Question-Answer – E-book NCERT
Population studies in Class 9 Geography Chapter 6 often feel tricky because there are so many terms – density, growth rate, distribution, and migration patterns. To make it easier, I’ve prepared notes that explain these concepts in a straightforward way with examples you’ll actually remember. The notes highlight key trends in India’s population and why they matter for understanding resources and development. They’re structured to help you revise quickly before exams without feeling lost in long paragraphs. You can easily download the NCERT Geography for Class 9th Chapter 6 Population Notes PDF and keep everything handy for clear, focused preparation.
Population Size And Distribution
India’s Population Size and Distribution by Numbers
1. Population Size (2011 Census):
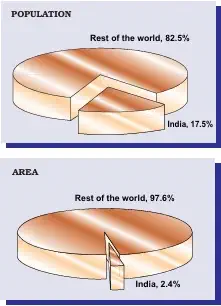
- India’s population (March 2011) = 1,210.6 million (1.21 billion).
- India accounts for more than 17% of the world’s population.
- India’s total area = 3.28 million sq. km (only 2.4% of the world’s area).
- India has 17% of the world’s people on 2.4% of the world’s area – indicates high population pressure.
2. Population Distribution (2011 Census):
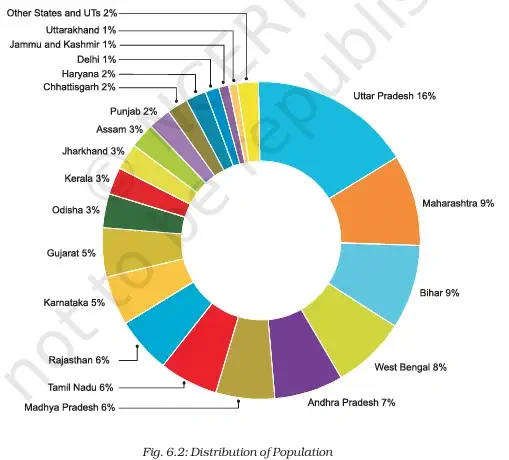
- Uttar Pradesh – most populous state: 199 million people.
- UP alone accounts for 16% of India’s population.
- Sikkim – population: 0.6 million (least populous state).
- Lakshadweep – population: 64,429 people (least populous Union Territory).
- Almost half of India’s population lives in just 5 states:
a. Uttar Pradesh
b. Maharashtra
c. Bihar
d. West Bengal
e. Andhra Pradesh - Rajasthan – India’s largest state by area, but has only 5.5% of India’s total population.
3. Census in India:
- Definition – A census is an official enumeration (counting) of population done periodically.
- First census in India – 1872 (not complete).
- First complete census – 1881.
- Since 1881, census is conducted regularly every 10 years.
- The Indian Census is the most comprehensive source of demographic, social, and economic data.
India’s Population Distribution by Density
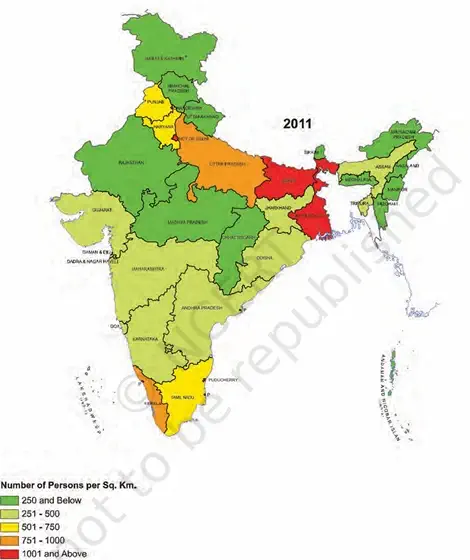
1. Concept & Definition:
- Population density = number of persons per unit area.
- It gives a clearer picture of uneven population distribution than total numbers.
2. Population Density of India (2011 Census):
- India = one of the most densely populated countries of the world.
- Average density (2011) = 382 persons per sq. km.
- Only Bangladesh and Japan have higher average population densities than India.
3. State-wise Variation (2011 Census):
- Bihar – highest density = 1,102 persons per sq. km.
- Arunachal Pradesh – lowest density = 17 persons per sq. km.
- States with density below 250 persons per sq. km: Sparse population due to rugged terrain and unfavourable climate.
- Assam + most of the Peninsular states – moderate densities.
a. Reasons: hilly, dissected, rocky terrain; moderate/low rainfall; shallow and less fertile soils. - Northern Plains + Kerala (South) – high to very high densities.
a. Reasons: flat plains, fertile soils, abundant rainfall. - Three states of the Northern Plains with high population density (to be identified by students, but from map/study: Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal).
4. Important Notes:
- Telangana became the 29th State of India in June 2014.
- Jammu and Kashmir was bifurcated into two Union Territories – Jammu & Kashmir, and Ladakh on 5 August 2019.
Next & Previous Topics of NCERT/CBSE Geography Class 9 Chapter 6: Population
| Topics No. | Topics Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Population Size And Distribution |
| 2 | Population Growth And Processes Of Population Change |
MCQs on NCERT Geography Class 9 Chapter 6 Topic – Population Size And Distribution
Here are the top exam-oriented MCQ-type questions on “Population Size And Distribution” that you should prepare for your CBSE or state board exams:
Question 1. What was India’s population as per the 2011 Census?
a) 1,000.6 million
b) 1,150.6 million
c) 1,210.6 million
d) 1,300 million
Answer: c) 1,210.6 million
Question 2. India’s population accounts for what percentage of the world’s population?
a) 15%
b) 16%
c) 17%
d) 20%
Answer: c) 17%
Question 3. What is the total area of India?
a) 2.8 million sq km
b) 3.28 million sq km
c) 4.2 million sq km
d) 3.5 million sq km
Answer: b) 3.28 million sq km
Question 4. India accounts for what percentage of the world’s area?
a) 2%
b) 2.4%
c) 3%
d) 3.4%
Answer: b) 2.4%
Question 5. Which state is the most populous in India as per 2011 Census?
a) Maharashtra
b) Bihar
c) Uttar Pradesh
d) West Bengal
Answer: c) Uttar Pradesh
Question 6. What was the population of Uttar Pradesh in 2011?
a) 150 million
b) 175 million
c) 199 million
d) 210 million
Answer: c) 199 million
Question 7. Uttar Pradesh accounts for about what percentage of India’s population?
a) 10%
b) 12%
c) 16%
d) 18%
Answer: c) 16%
Question 8. Which state had the least population in 2011?
a) Goa
b) Nagaland
c) Sikkim
d) Manipur
Answer: c) Sikkim
Question 9. What was the population of Sikkim in 2011?
a) 0.2 million
b) 0.4 million
c) 0.6 million
d) 1 million
Answer: c) 0.6 million
Question 10. The Union Territory with only 64,429 people as per 2011 was:
a) Andaman and Nicobar
b) Lakshadweep
c) Daman and Diu
d) Puducherry
Answer: b) Lakshadweep
Question 11. Almost half of India’s population lives in which five states?
a) UP, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh
b) UP, Rajasthan, Punjab, Kerala, Odisha
c) Bihar, MP, Karnataka, Gujarat, Assam
d) Maharashtra, Kerala, Punjab, Haryana, Tamil Nadu
Answer: a) UP, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh
Question 12. Rajasthan accounts for what percent of India’s total population?
a) 5.5%
b) 6%
c) 7%
d) 10%
Answer: a) 5.5%
Question 13. What is a census?
a) Estimation of animals
b) Enumeration of population done periodically
c) Collection of rainfall data
d) Economic growth calculation
Answer: b) Enumeration of population done periodically
Question 14. In which year was the first census held in India?
a) 1857
b) 1861
c) 1872
d) 1881
Answer: c) 1872
Question 15. The first complete census in India was taken in:
a) 1872
b) 1881
c) 1891
d) 1901
Answer: b) 1881
Question 16. How frequently is the Indian Census held?
a) Every 5 years
b) Every 7 years
c) Every 10 years
d) Every 12 years
Answer: c) Every 10 years
Question 17. Which is the most comprehensive source of demographic, social and economic data in India?
a) National Sample Survey
b) NITI Aayog Report
c) Census
d) Economic Survey
Answer: c) Census
Question 18. What was India’s population density in 2011?
a) 250 persons per sq km
b) 300 persons per sq km
c) 382 persons per sq km
d) 400 persons per sq km
Answer: c) 382 persons per sq km
Question 19. Which state had the highest population density in 2011?
a) West Bengal
b) Kerala
c) Uttar Pradesh
d) Bihar
Answer: d) Bihar
Question 20. What was the population density of Bihar in 2011?
a) 850 persons/sq km
b) 1,102 persons/sq km
c) 950 persons/sq km
d) 1,000 persons/sq km
Answer: b) 1,102 persons/sq km
Question 21. Which state had the lowest population density in 2011?
a) Mizoram
b) Sikkim
c) Arunachal Pradesh
d) Nagaland
Answer: c) Arunachal Pradesh
Question 22. What was the population density of Arunachal Pradesh in 2011?
a) 17 persons/sq km
b) 25 persons/sq km
c) 50 persons/sq km
d) 100 persons/sq km
Answer: a) 17 persons/sq km
Question 23. States with population densities below 250 persons/sq km usually have:
a) Fertile soils and abundant rainfall
b) Rugged terrain and unfavourable climate
c) Dense forests and mineral wealth
d) Advanced industries
Answer: b) Rugged terrain and unfavourable climate
Question 24. Assam and most Peninsular states have what kind of population density?
a) Very high
b) High
c) Moderate
d) Low
Answer: c) Moderate
Question 25. What factors influence moderate densities in Peninsular states?
a) Flat plains and heavy rainfall
b) Hilly terrain, low rainfall, less fertile soils
c) Desert climate
d) Dense forest cover
Answer: b) Hilly terrain, low rainfall, less fertile soils
Question 26. Which regions have high to very high population densities in India?
a) Rajasthan desert and Himalayan belt
b) Northern Plains and Kerala
c) Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh
d) Central plateau and coastal Odisha
Answer: b) Northern Plains and Kerala
Question 27. Why do Northern Plains have very high densities?
a) Desert land with minerals
b) Flat plains, fertile soils, abundant rainfall
c) Mountain ranges with rivers
d) Industrial hubs only
Answer: b) Flat plains, fertile soils, abundant rainfall
Question 28. Which two countries have higher average population density than India?
a) China and Japan
b) Bangladesh and Japan
c) Nepal and Sri Lanka
d) Pakistan and Myanmar
Answer: b) Bangladesh and Japan
Question 29. Telangana became the 29th state of India in:
a) 2012
b) 2013
c) 2014
d) 2015
Answer: c) 2014
Question 30. The State of Jammu and Kashmir was bifurcated into two Union Territories in:
a) 2016
b) 2018
c) 2019
d) 2020
Answer: c) 2019
Question 31. The two UTs formed after bifurcation of J&K are:
a) Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh
b) Jammu & Kashmir and Chandigarh
c) Ladakh and Puducherry
d) Jammu & Kashmir and Daman & Diu
Answer: a) Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh

